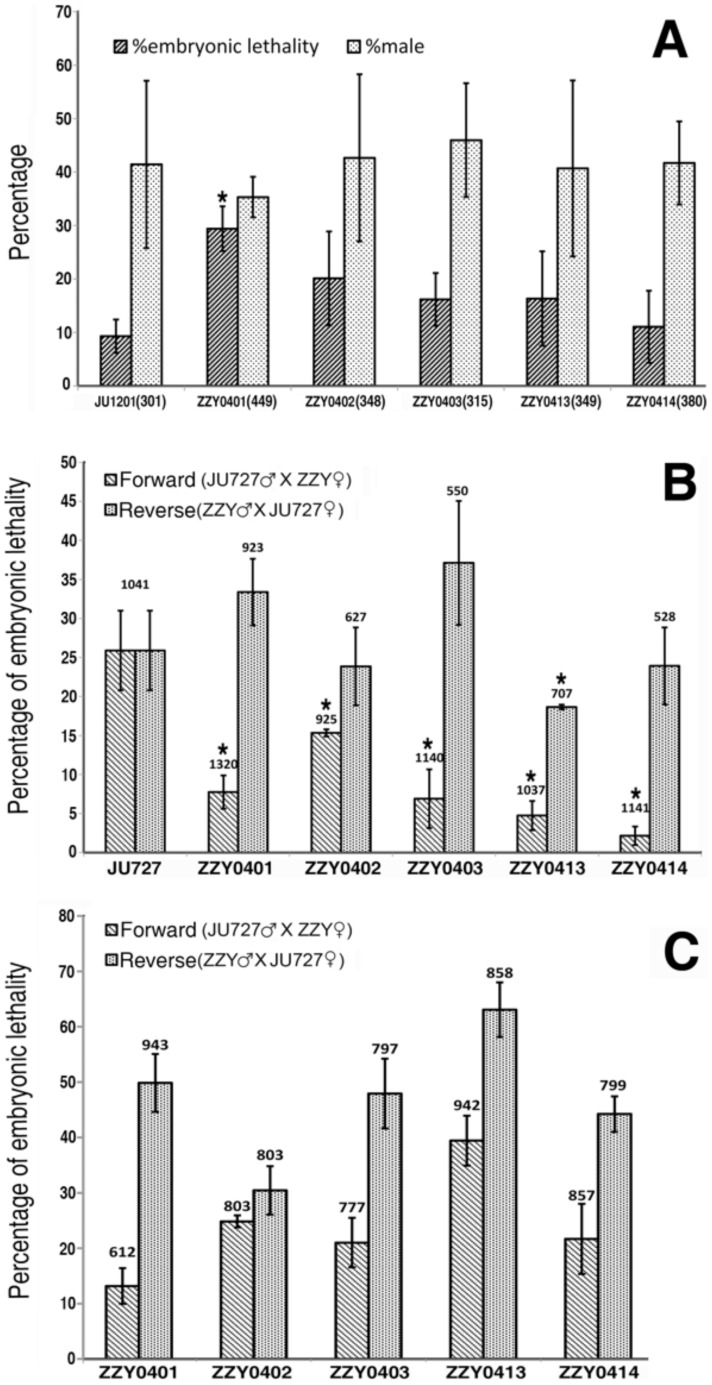
Figure 4. Hybrid viability between our five wild isolates and Caenorhabditis sinica sp. n. reference strains.
A: percentage of male and embryonic lethality for C. sinica sp. n. (JU1201) itself and its F1 crossing progeny with our five wild isolates. Shown are data derived from one crossing direction, i.e., crossing between JU1201 males and ZZY females. Significant difference (p<0.05, Student's t test) between JU1201 and the crossing progeny is indicated with “*”. Numbers of adult progeny counted are indicated in the bottom (in parenthesis). Error bars denote standard deviations. B and C: percentage of embryonic lethality of F1 and F2 hybrid progeny between C. sinica sp. n. (JU727) and the five wild isolates respectively. Crossings were performed in both forward and reverse directions as indicated (See Materials and Methods for details). F1 hybrid males and females derived from the crossing in either direction were mated and F2 embryonic lethality was scored for their progeny. Significant difference (p<0.05, Student's t test) in the percentage of embryonic lethality between JU727 and the crossing progeny is marked with “*”. Numbers of total embryos counted are indicated above each bar.