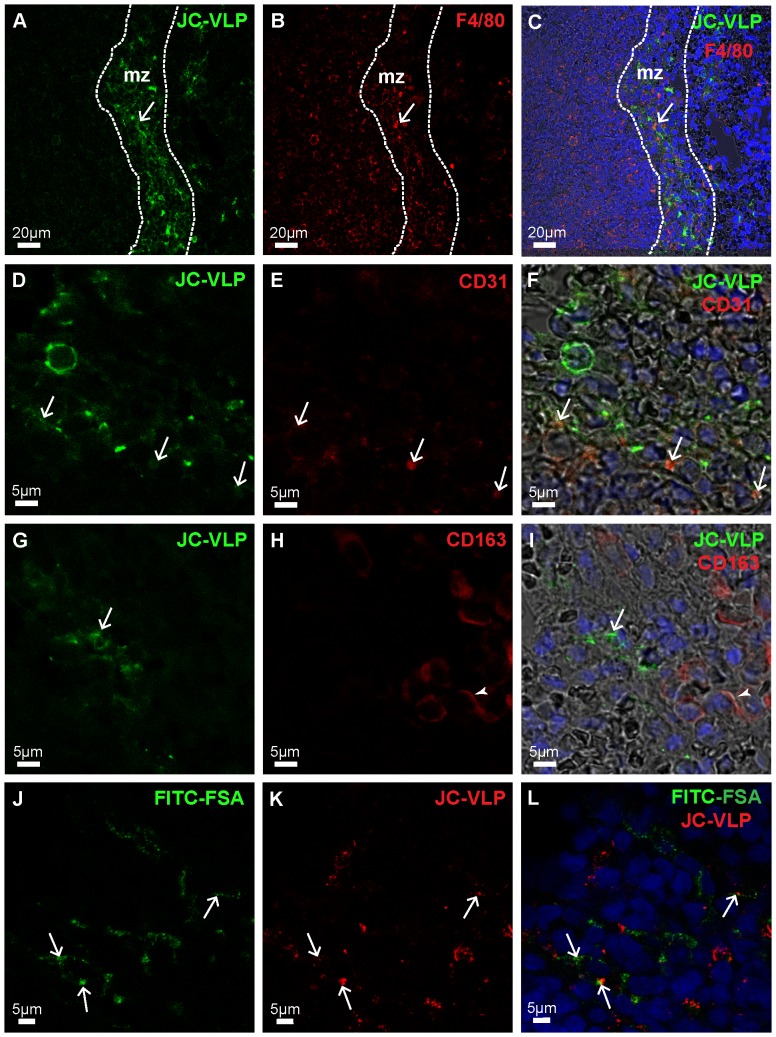
Figure 9. JC-VLP uptake in spleen.
Panels A–I: Mouse tissues were perfusion fixed 7 min after intravenous injection of JC-VLPs. Paraffin sections of spleen were double immune labeled using a rabbit antiserum against BK-VP1 [53] (reacts also with JC-VP1), and antibodies against F4/80 (A–C), CD31 (D–F) or CD163 (G–I). Antibodies are listed in Table 1. The VP1 staining pattern (green) showed that the uptake of VLPs was concentrated in the red pulp marginal zone, mz (A), and here partly co-localized with F4/80 (C, arrow), and CD31 (F, arrows), but not with CD163 (I; arrow indicates VP1, and arrow head to CD163 staining). The F4/80 (B, C), CD31 (E, F), and CD163 (H, I) staining patterns are all shown in red. Panels J–L: In J–L, tail vein injection of JC-VLPs was followed by injection of FITC-FSA in the opposite tail vein and tissues perfusion fixed 15 min after the VLP administration. Both JC-VLP (K; red fluorescence) and FITC-FSA (J; green fluorescence) distributed to the reticuloendothelial network of the spleen red pulp marginal zone (L; arrows point to overlap of JC-VLP staining and FITC-FSA uptake).