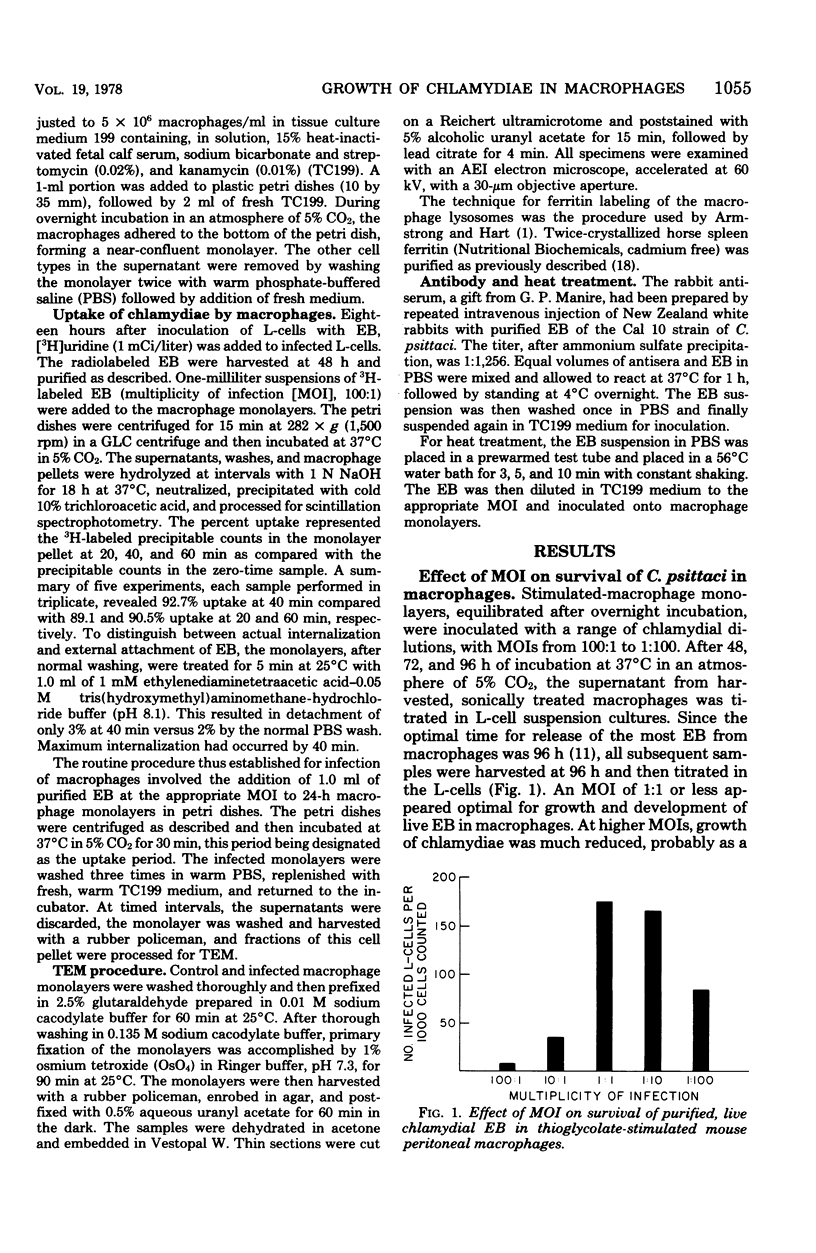
Abstract
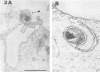
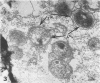
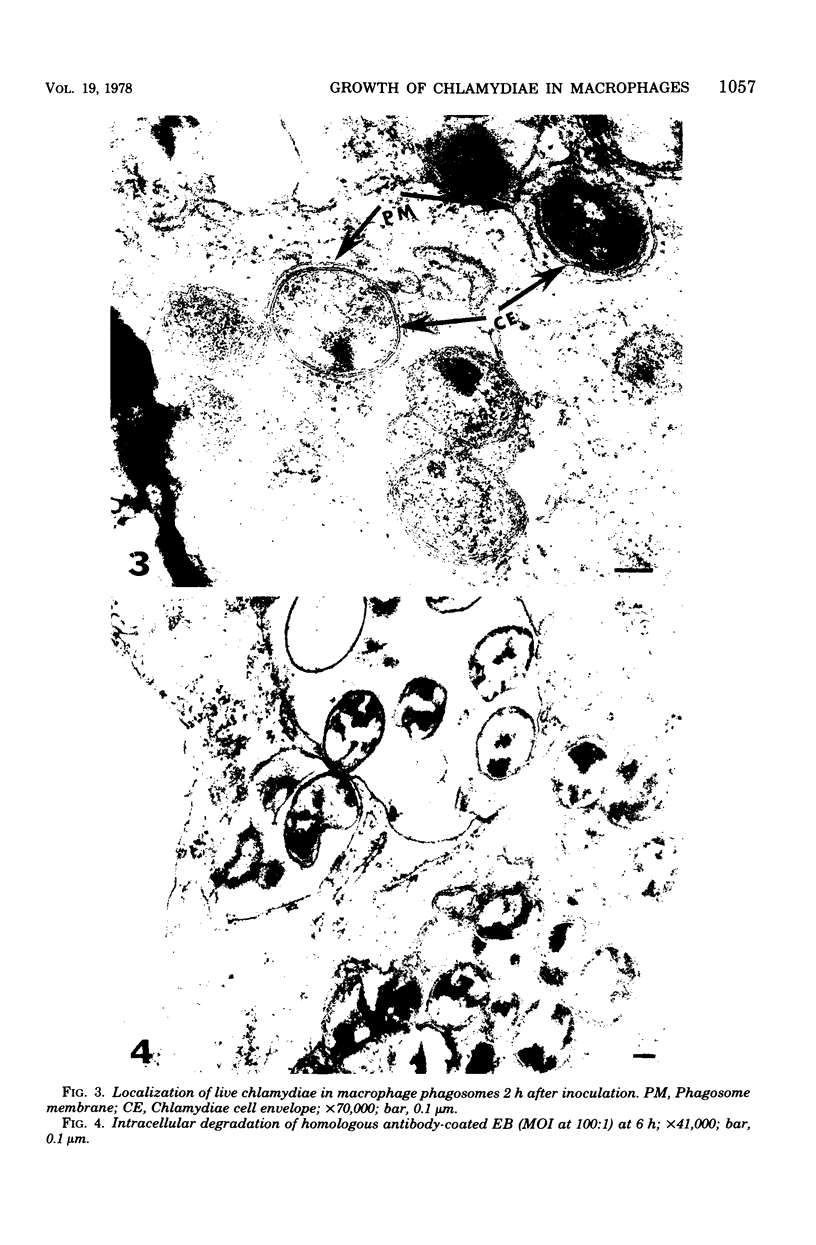
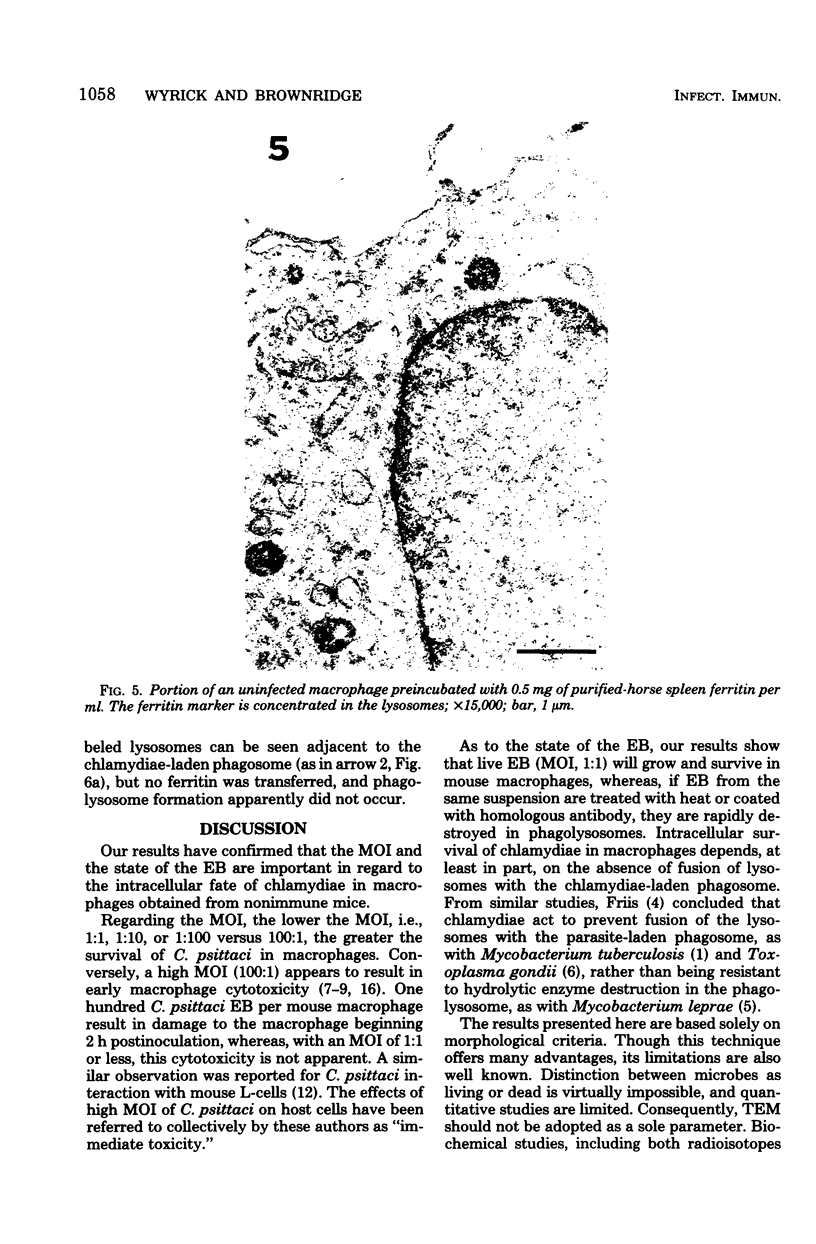
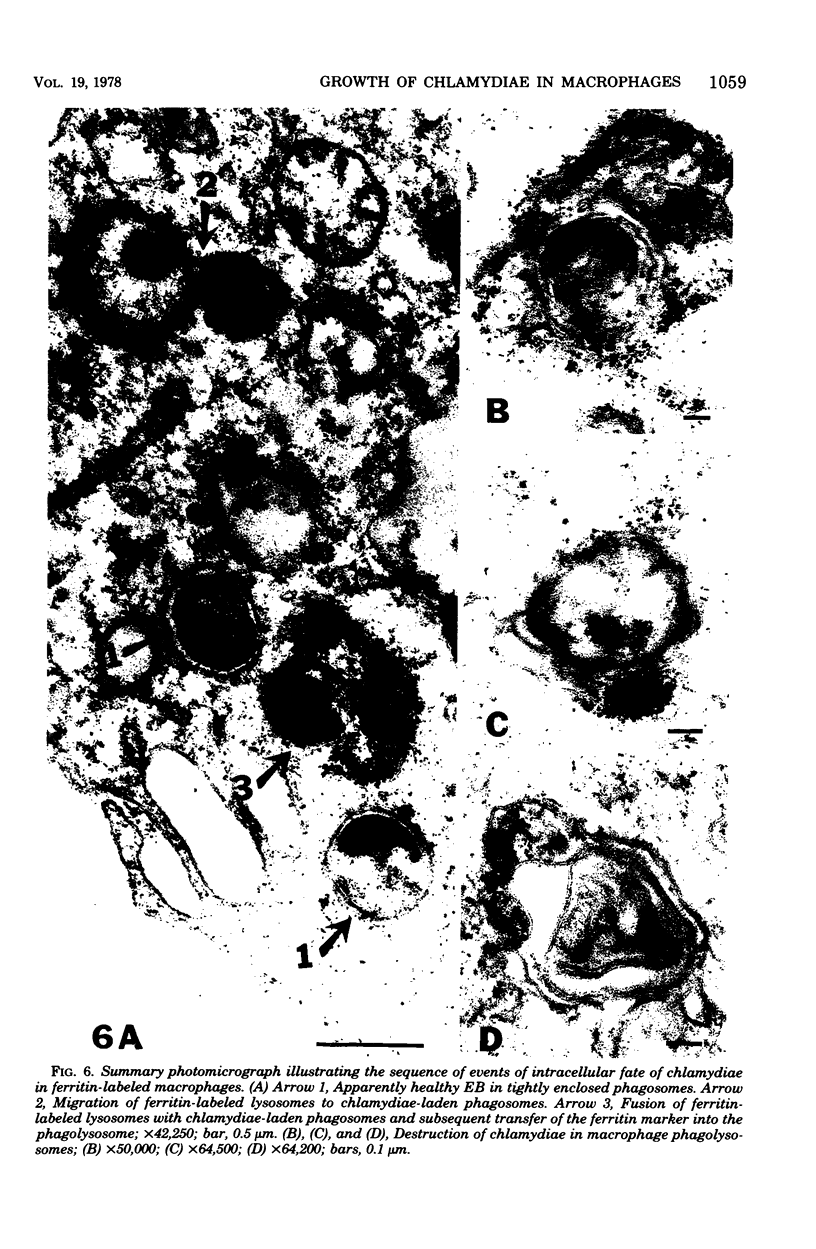
Survival and growth of L-cell-cultivated Chlamydia psittaci occurred in mouse macrophages in vitro. Two major factors governing the intracellular fate of chlamydiae in macrophages are: (i) the multiplicity of infection (MOI), i.e., the elementary body (EB)-to-macrophage ratio, and (ii) the state of the EB. At a low MOI (1:1) survival and growth of live, untreated chlamydiae were optimal. The chlamydiae were internalized in macrophages within 30 to 40 min. EB proceeded to differentiate into reticulate bodies, which underwent multiplication and further matured into infectious EB in the professional phagocytic cells. In contrast, at a high MOI (100:1), survival of untreated chlamydiae was greatly reduced as a result of immediate damage to the macrophages. eb that were pretreated with heat (56 degrees C for 10 to 30 min) or coated with homologous antibody were rapidly destroyed in macrophage phagolysosomes. Fusion of ferritin-labeled lysosomes with heat-treated or opsonized EB-laden phagosomes occurred in 2 to 4 h, resulting in transfer of the ferritin marker into phagolysosomes.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong J. A., Hart P. D. Response of cultured macrophages to Mycobacterium tuberculosis, with observations on fusion of lysosomes with phagosomes. J Exp Med. 1971 Sep 1;134(3 Pt 1):713–740. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.3.713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENEDICT A. A., McFARLAND C. Growth of meningopneumonitis virus in normal and immune guinea pig monocytes. Nature. 1958 Jun 21;181(4625):1742–1743. doi: 10.1038/1811742a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHN Z. A., BENSON B. THE DIFFERENTIATION OF MONONUCLEAR PHAGOCYTES. MORPHOLOGY, CYTOCHEMISTRY, AND BIOCHEMISTRY. J Exp Med. 1965 Jan 1;121:153–170. doi: 10.1084/jem.121.1.153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friis R. R. Interaction of L cells and Chlamydia psittaci: entry of the parasite and host responses to its development. J Bacteriol. 1972 May;110(2):706–721. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.2.706-721.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart P. D., Armstrong J. A., Brown C. A., Draper P. Ultrastructural study of the behavior of macrophages toward parasitic mycobacteria. Infect Immun. 1972 May;5(5):803–807. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.5.803-807.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. C., Hirsch J. G. The interaction between Toxoplasma gondii and mammalian cells. II. The absence of lysosomal fusion with phagocytic vacuoles containing living parasites. J Exp Med. 1972 Nov 1;136(5):1173–1194. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.5.1173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kordová N., Hoogstraten J., Wilt J. C. Lysosomes and the "toxicity" of Rickettsiales. IV. Ultrastructural studies of macrophages infected with a cytopathic L cell-grown C. psittaci 6BC strain. Can J Microbiol. 1973 Mar;19(3):315–320. doi: 10.1139/m73-052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kordová N., Poffenroth L., Wilt J. C. Lysosomes and the "toxicity" of rickettsiales. II. Non-cytocidal interactions of egg-grown C. psittaci 6BC and in vitro macrophages. Can J Microbiol. 1972 Jun;18(6):869–873. doi: 10.1139/m72-134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kordová N., Wilt J. C. Lysosomes and the "toxicity" of Rickettsiales. I. Cytochemical studies of macrophages inoculated in vitro with C. psittaci 6BC. Can J Microbiol. 1972 Apr;18(4):457–464. doi: 10.1139/m72-071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo C. C., Grayston T. Interaction of Chlamydia trachomatis organisms and HeLa 229 cells. Infect Immun. 1976 Apr;13(4):1103–1109. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.4.1103-1109.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lépinay A., Orfila J., Anteunis A., Boutry J. M., Orme-Roselli L., Robineaux R. Etude en microscopie électronique du développement et de la morphologie de Chlamydia psittaci dans les macrophages de souris. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1970 Aug;119(2):222–231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moulder J. W., Hatch T. P., Byrne G. I., Kellogg K. R. Immediate toxicity of high multiplicities of Chlamydia psittaci for mouse fibroblasts (L cells). Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):277–289. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.277-289.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAMURA A., HIGASHI N. PURIFICATION AND CHEMICAL COMPOSITION OF MENINGOPNEUMONITIS VIRUS. Virology. 1963 Aug;20:596–604. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taverne J., Blyth W. A., Ballard R. C. Interactions of TRIC agents with macrophages: effects on lysosomal enzymes of the cell. J Hyg (Lond) 1974 Apr;72(2):297–309. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400023512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd W. J., Storz J. Ultrastructural cytochemical evidence for the activation of lysosomes in the cytocidal effect of Chlamydia psittaci. Infect Immun. 1975 Sep;12(3):638–646. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.3.638-646.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyrick P. B., Brownridge E. A., Ivins B. E. Interaction of Chlamydia psittaci with mouse peritoneal macrophages. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):1061–1067. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.1061-1067.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]