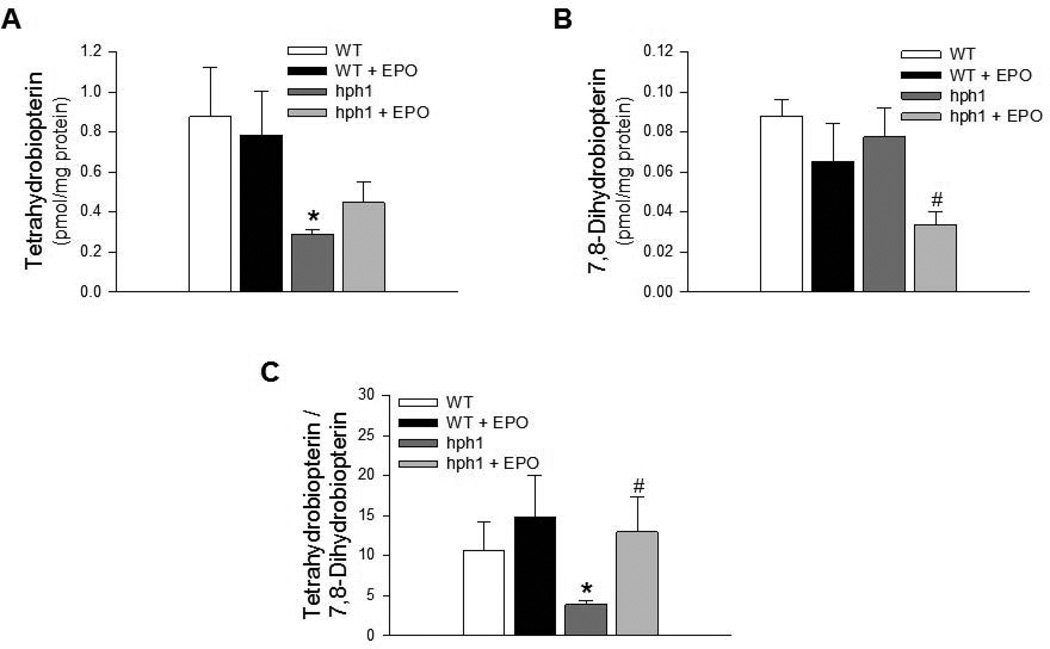
Figure 1.
Treatment with EPO increased BH4 bioavailability. A) BH4 levels in cerebral microvessels of hph1 mice were significantly reduced (* P<0.05 vs. WT, n =6). EPO treatment did not affect BH4 levels in cerebral microvessels of wild-type mice and hph1 mice. B) EPO inhibited oxidation of BH4, as indicated by the significantly reduced levels of 7,8-dihydrobiopterin in cerebral microvessels of hph1 mice treated with EPO (# P<0.05 vs. hph1, n=6). C) The ratio of BH4 to 7,8-BH2, indicative of BH4 bioavailability, was significantly decreased in cerebral microvessels of hph1 mice (* P<0.05 vs. WT, n=6). Treatment with EPO significantly increased the ratio of BH4 to 7,8-BH2 in cerebral microvessels of hph1 mice (# P<0.05 vs. hph1, n=6).