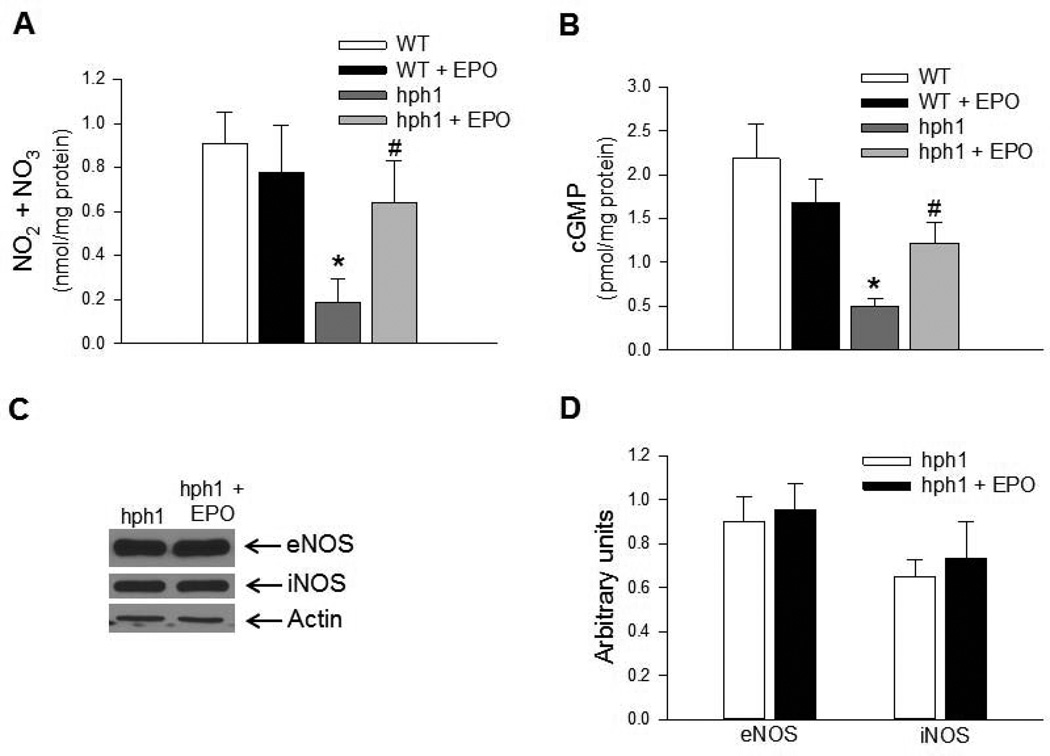
Figure 4.
Treatment with EPO increased bioavailability of endothelial NO in cerebral microvessels of hph1 mice. A) Levels of total nitrite/nitrate were significantly reduced in cerebral microvessels of hph1 mice (* P<0.05 vs. WT, n=6). While EPO treatment did not affect total nitrite/nitrate levels in cerebral microvessels of wild-type mice, levels of NOx in cerebral microvessels of hph1 mice were significantly increased (# P<0.05 vs. hph1, n=6). B) Basal levels of cGMP were significantly attenuated in cerebral microvessels of hph1 mice (* P<0.05 vs. WT, n=8–9). Treatment with EPO significantly increased levels of cGMP in cerebral microvessels of hph1 mice (# P<0.05 vs. hph1, n=8), while the levels of cGMP in wild-type mice remained unchanged following EPO treatment. C) Representative Western blots demonstrating that EPO treatment did not affect expressions of eNOS or iNOS in cerebral microvessels of hph1 mice. D) Bar diagram representing the densitometric analysis of eNOS and iNOS expressions in cerebral microvessels of hph1 mice treated with EPO.