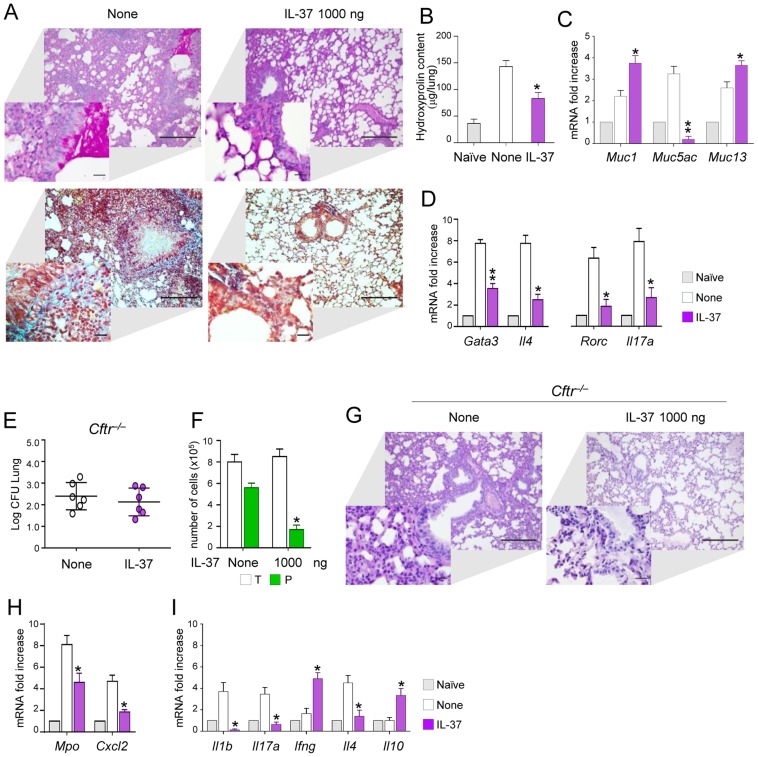
Figure 6. IL-37 restrains inflammation in fungal allergy and Cftr−/− mice.
(A) Lung histology (PAS- and Masson's trichrome-stained sections, scale bars 100 and 25 (insets) µm); (B) hydroxyproline content (µg/lung); (C) expression of mucins (RT-PCR on total lung cells); (D) expression of cytokines and Th transcription factors in total lung cells from mice with ABPA and treated with IL-37. None, untreated mice. Naïve, uninfected and untreated mice. (E) Fungal growth (Log10 CFU, mean±SD) in the lungs of Cftr−/− mice infected intranasally with A. fumigatus and treated intraperitoneally with IL-37, at the dose of 1000 ng/mouse, 1 hour before the infection. (F) BAL fluid morphometry [number of total (T) cells and polymorphonuclear neutrophils (P) upon May Grunwald Giemsa staining]. (G) Lung histology (periodic acid-Schiff staining) and cell recruitment (insets). Scale bars, 100 µm and 25 µm in the insets; (H) Mpo and Cxcl2 mRNA expression and (I) cytokine gene expression on total lung cells by RT-PCR, 3 days after the infection. Data are pooled from two experiments. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, treated vs untreated (None) mice. Naïve, uninfected and untreated mice.