Figure 2.
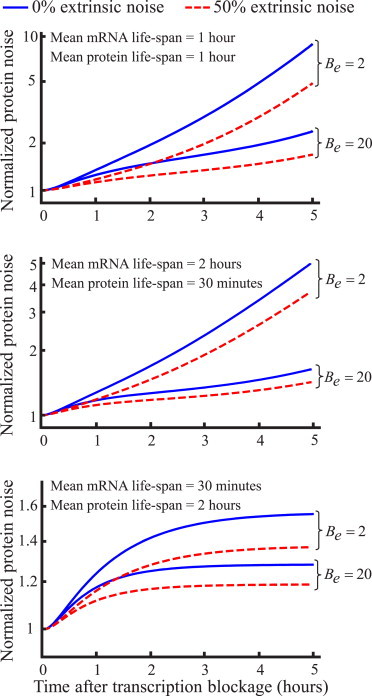
Transient changes in protein copy number variation after transcription blockage identifies noise mechanisms. Protein noise level ((t)) monotonically increases after mRNA production is blocked. Shape of (t) for different percentages of extrinsic noise (/) and Be (extent of transcriptional bursting) are shown, with higher values of Be and resulting in a lower rate of increase. Low (high) transcriptional bursting corresponds to Be = 2(20). Protein noise levels are normalized by their values at t = 0 given by (0) = . Three cases of protein (γp) and mRNA (γm) degradation rates are considered: γp = γm (top); γp = 2 h−1, γm = 0.5 h−1 (middle); and γp = 0.5 h−1, γm = 1 h−1 (bottom). To see this figure in color, go online.
