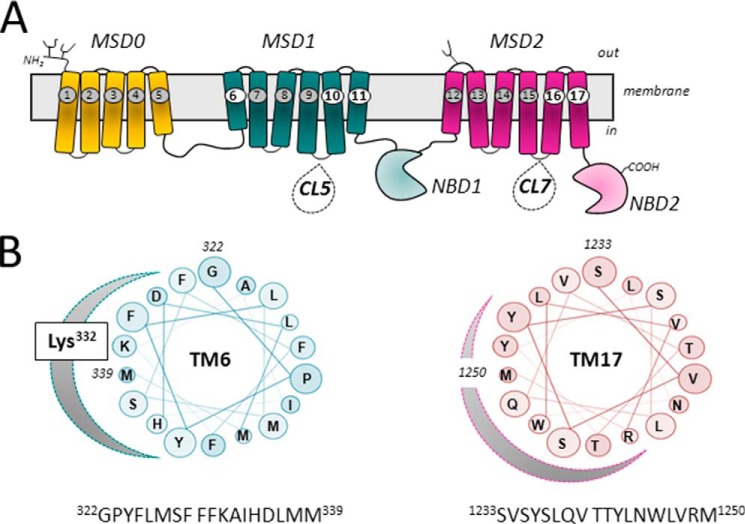
FIGURE 1.
Topology of MRP1 and projections of amphipathic TM α-helices 6 and 17. A, shown is a schematic diagram of a predicted secondary structure of MRP1/ABCC1. The positions of TMs 6, 10, 11, 16, and 17, which have been identified as containing key determinants of MRP1 substrate specificity, are highlighted. Also indicated are CL5 and CL7, which contain amino acids involved in substrate specificity, proper folding, and plasma membrane trafficking, as well as the transport mechanism of MRP1. B, shown are helical wheel projections of 18 amino acids of the amphipathic TM6 (in MSD1) and TM17 (in MSD2) of MRP1. The clustering on one side of each TM helix of polar residues with side chains capable of H-bonding is indicated by the shaded curve. Highlighted on the projection of TM6 is Lys332, which is particularly critical for LTC4 and GSH transport (43, 51).