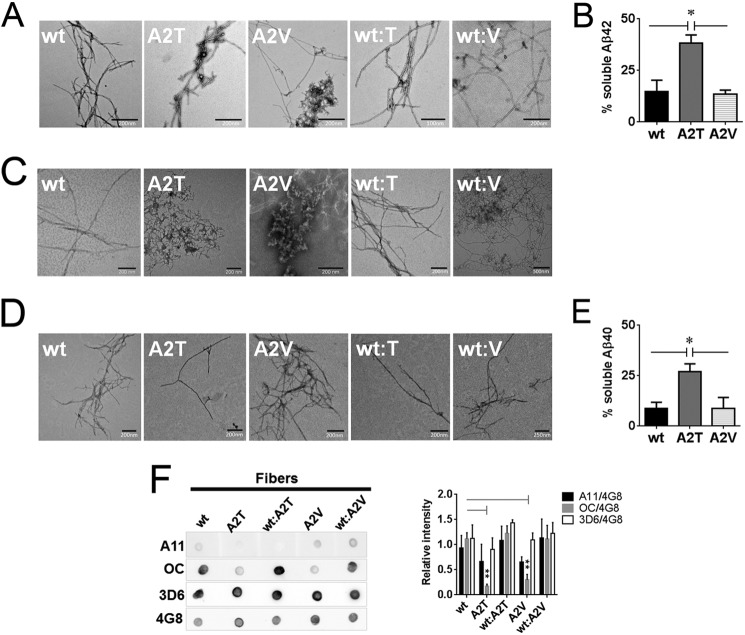
FIGURE 8.
Impact of the A2T and A2V mutations on the morphology and residual soluble peptide content in aggregated Aβ variants. A, transmission electron micrographs of the fibers obtained after 2 weeks of quiescent incubation of Aβ42 variants and their equimolar mixes with the wild type Aβ42. B, residual soluble peptide content in Aβ42 variants incubated at concentrations above 50 μm for 2 weeks. Significance (unpaired two-tailed t test) is indicated by *, p < 0.05, means + S.E., n = 3. C, transmission electron micrographs of the fibers formed by Aβ40 variants and their equimolar mixes with the wild type Aβ40 after 2 weeks and 6 weeks (D) of quiescent incubation. E, residual soluble peptide content in Aβ40 mutants incubated at 100 μm for 6 weeks. Significance (unpaired two-tailed t test) is indicated by *, p < 0.05, means + S.E., n = 3. F, immune dot blot of Aβ42 fibers. Aβ was incubated in Tris/EDTA buffer, pH 7.4, for 2 weeks, blotted on a nitrocellulose membrane, and probed with conformation-specific antibodies A11 and OC. 4G8 antibody was used as a loading control. 3D6 antibody recognizing the first five amino acids of Aβ was used to probe N-terminal accessibility in mutant aggregates. Immune reactivity of Aβ40 fibers did not change between 2 and 6 weeks of aggregation and was identical to the one of Aβ42. Right panel: densitometric analysis of Aβ fiber dot blots. OC reactivity of the mutant fibers is significantly diminished compared with the WT fibers (unpaired two-tailed t test; **, p < 0.01, means + S.E., n = 3–4). A11 signal intensities of fibers can be considered negligible.