FIGURE 6.
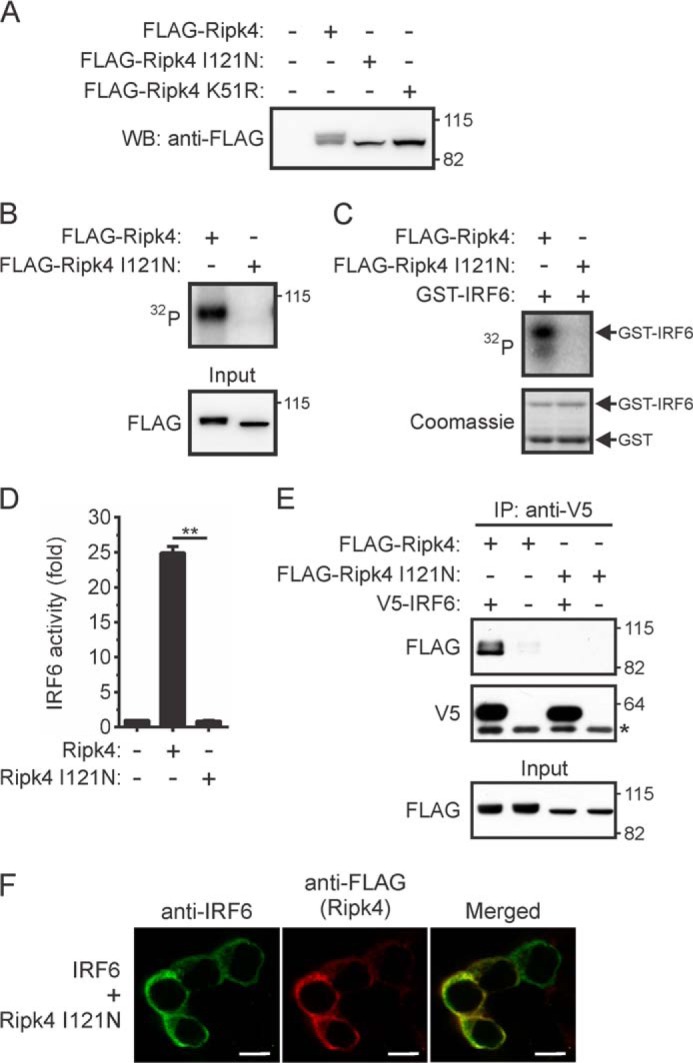
Effects of a BPS-associated mutation on the activation of IRF6 by RIPK4. A–C, HEK293T cells transiently expressing FLAG-Ripk4, FLAG-Ripk4 I121N, or FLAG-Ripk4 K51R were lysed 24 h post-transfection. A, the lysates were subjected to Western blotting (WB) with an anti-FLAG antibody. The positions of molecular weight standards (in kilodaltons) are indicated. B and C, FLAG-Ripk4 and FLAG-Ripk4 I121N were immunoprecipitated from the lysates using anti-FLAG antibodies and their abilities to autophosphorylate (B) and phosphorylate GST-IRF6 CTD (C) were measured. The data are representative of two independent experiments. D, HEK293T cells were transfected with an IFNβ gene promoter reporter plasmid together with expression vectors encoding IRF6 and either Ripk4 or Ripk4 I121N. Gene reporter activity was measured 24 h post-transfection, and IRF6 activity is shown as the fold increase. **, p < 0.01. The data are combined from three independent experiments. E, HEK293T cells transiently expressing the indicated proteins were lysed 24 h post-transfection. IRF6 was immunoprecipitated (IP) from the lysates using anti-V5 antibodies, followed by Western blotting with anti-FLAG and anti-V5 antibodies. The asterisk indicates the position of the anti-V5 antibody heavy chain. The lysates (input) were subjected to Western blotting with an anti-FLAG antibody. The data are representative of three independent experiments. F, HEK293T cells transiently coexpressing IRF6 and Ripk4 I121N were stained with antibodies against IRF6 (green) and anti-FLAG (red) antibodies. Scale bars = 10 μm. The data are representative of four independent experiments.
