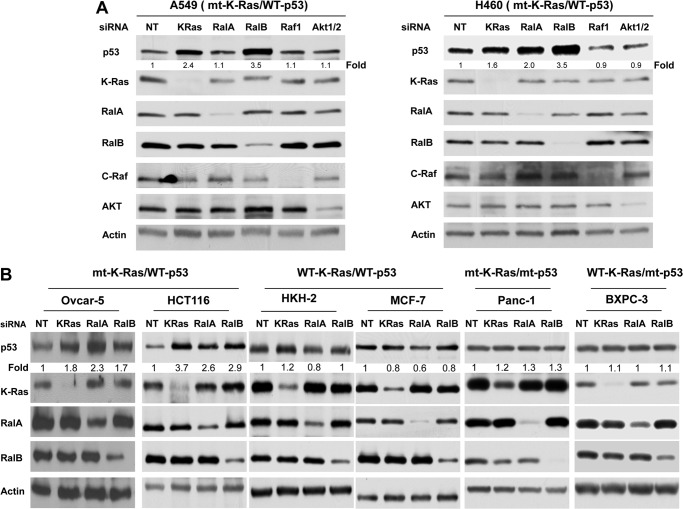
FIGURE 1.
Depletion of RalA and/or RalB increases p53 protein levels in cancer cells with wild-type p53 and mutant (mt) K-Ras. A, depletion of RalA and/or RalB but not AKT1/2 or c-Raf affects p53 protein levels in cells with mt K-Ras and WT p53. H460 and A549 cells were transfected with indicated siRNAs for 48 h and processed for Western blot analysis as described under “Experimental Procedures.” B, cancer cells that harbor mt K-Ras and WT p53 (HCT116 colon cancer cells and OVCAR-5 ovarian cancer cells), WT K-Ras and WT p53 (HKH2 and MCF7 breast cancer cells), WT K-Ras and mt p53 (BXPC3 pancreatic cancer cells), and mt K-Ras and mt p53 (Panc-1 pancreatic cancer cells) were transfected with the indicated siRNAs for 48 h and processed for Western blot analysis as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Data are representative of three (A549, H460, and HCT116) or two (OVCAR-5, Panc-1, HKH2, MCF7, and BXPC3) independent experiments. In H460 cells, densitometry quantification shows that depletion of K-Ras, RalA, and RalB increased p53 levels by 2.16 ± 0.33-, 2.23 ± 0.18-, and 3.36 ± 0.11-fold, respectively. These increases were statistically significant with p values of less than 0.05, 0.01, and 0.01, respectively. In A549 cells, densitometry quantification shows that depletion of K-Ras and RalB increased p53 levels by 1.89 ± 0.26- and 2.40 ± 0.55-fold, respectively. These increases were statistically significant, with p values of less than 0.05 and 0.05, respectively. Depletion of RalA did not affect the levels of p53 (1.02 ± 0.07-fold) in A549 cells. NT, nontargeting.