FIGURE 7.
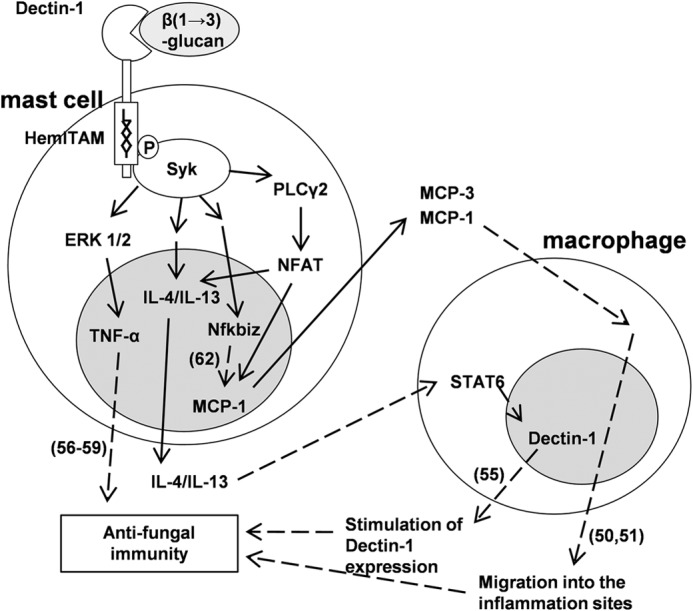
Dectin-1-mediated signaling in mast cells may directly and indirectly contribute to antifungal immunity. This schema shows dectin-1-mediated signal transduction and subsequent increase of transcription factor and cytokines revealed in this study. Solid arrows, results revealed in this study; dashed arrows, results revealed in past reports (reference numbers shown in parenthesis). Dectin-1 is expressed in mast cells and recognizes β(1→3)-glucan. Tyr15 in hemITAM of Dectin-1 is required for subsequent recruitment of the SH2 domains of Syk, resulting in tyrosine phosphorylation of Syk. Dectin-1/Syk signaling activates intracellular signal transducers involving PLCγ2, NFAT, and ERK1/2, resulting in stimulation of gene expression of cytokines and transcription factors, such as MCP-1, IL-3, IL-4, IL-13, TNF-α, and Nfkbiz. MCP-1, IL-4/IL-13, Nfkbiz, and TNF-α may assume induction of macrophage migration into the inflammation sites together with MCP-3, stimulation of Dectin-1 expression in macrophages, stimulation of MCP-1 gene expression, and inflammatory response against fungi, respectively. These events lead an individual to the successful control of fungal infections.
