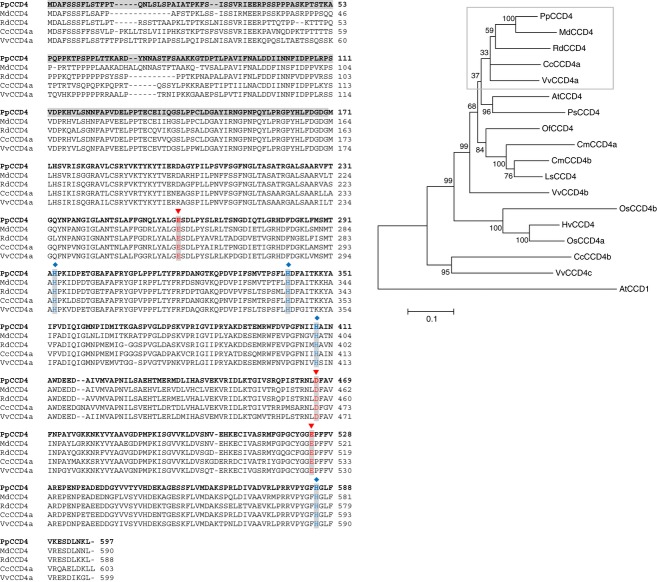
Figure 2.
UPGMA consensus tree and amino acid sequence comparison of CCD4 proteins of various plant species.
Left: amino acid sequence alignment of species closely related to peach. Gray-shaded amino acids represent the N–terminus of the manually predicted protein that is not present in the automated prediction of the peach genome sequence v1.0. The conserved four iron-ligating histidine (H) residues, and the glutamates (E) or aspartates (D) giving stability to the complex, are indicated (blue and red, respectively).
Right: phylogenetic tree showing bootstrap support at critical nodes as percentages. PpCCD4, Prunus persica (ppa006109); MdCCD4, Malus domestica (ABY47995); RdCCD4, Rosa damascena (ABY60886); CcCCD4a, Citrus clementina (ABC26011); AtCCD4, Arabidopsis thaliana (NP_193652); PsCCD4, Pisum sativum (BAC10552); VvCCD4a, Vitis vinifera (XP_002268404); OsCCD4, Osmanthus fragrans (ABY60887); CmCCD4a, Chrysanthemum morifolium (ABY60885); CmCCD4b, Chrysanthemum morifolium (BAF36656); LsCCD4, Lactuca sativa (BAE72094); VvCCD4b, Vitis vinifera (XP_002270161); OsCCD4b, Oryza sativa (ABA97976); HvCCD4, Hordeum vulgare (AK248229); OsCCD4a, Oryza sativa (NP_001047858); CcCCD4b, Citrus clementina (ABC26012); VvCCD4c, Vitis vinifera (XP_002269538); AtCCD1, Arabidopsis thaliana (NP_191911).