Figure 1.
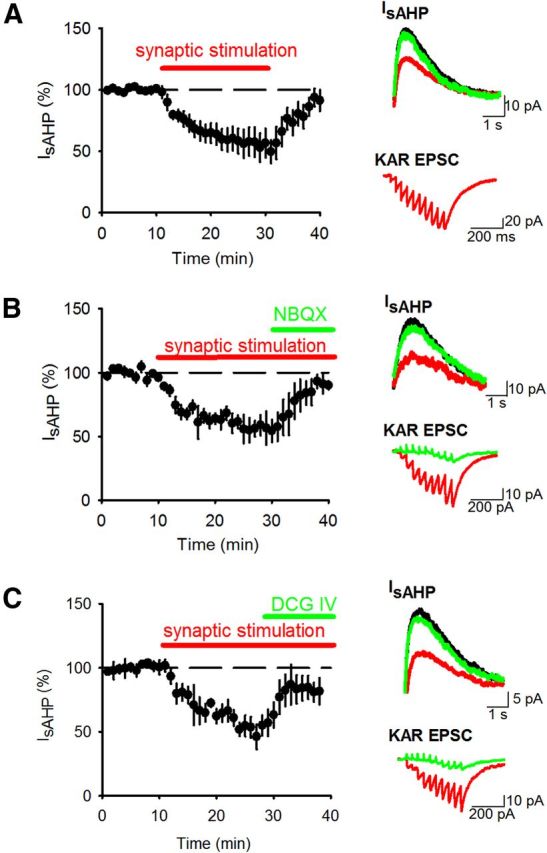
Synaptic KAR stimulation depresses IsAHP. A, IsAHPs were stimulated with 200 ms depolarizations to 0 mV from a holding potential of −60 mV. Synaptic stimulation of 10 stimuli at 25 Hz produced a depression in IsAHP. Example traces show IsAHPs (top) and synaptic responses (bottom) during baseline (black), synaptic stimulation (red) and after recovery (green). B, Application of NBQX (10 μm) to block KARs reversed the depression of IsAHP by synaptic stimulation. C, Application of DCG-IV (1 μm) to inhibit glutamate release from mossy fiber terminals reversed the depression of IsAHP by synaptic stimulation.
