Figure 6.
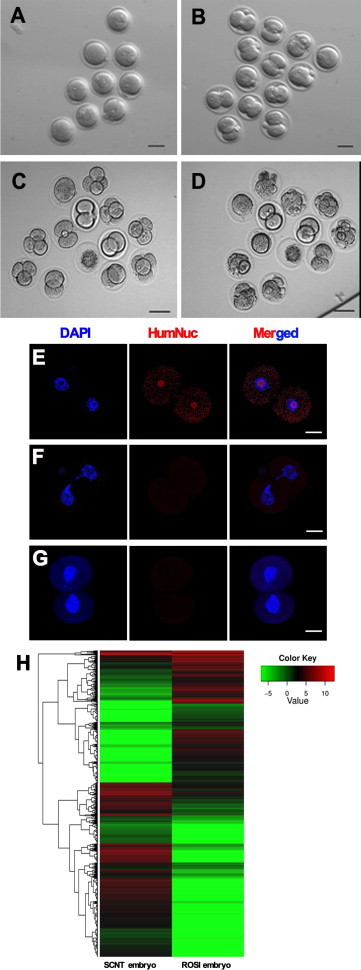
Developmental Potentials, HumNuc Expression, and Global Gene Expression Patterns of the Embryos from Mouse Oocytes Fertilized with Round Spermatids Derived from Human SSCs of Cryptorchid Patients
(A–D) Phase-contrast microscope showing the morphology of embryos with two pronuclei (PN) (A), embryos developing into the two-cell (B), four-cell (C), and eight-cell (D) stages. Scale bars in (A)–(D), 50 μm.
(E) Immunocytochemistry revealing the expression of HumNuc in the embryos from mouse oocytes fertilized with human round spermatids from human SSCs.
(F and G) Replacement of HumNuc antibody with normal rabbit IgG (F) or PBS (G) in the embryos from mouse oocytes fertilized with human round spermatids served as negative controls. Scale bars in (E)–(G), 25 μm.
(H) Clustering of the transcriptome of single embryo derived from round spermatids of cryptorchid patients and from the nucleus of Sertoli cells by single-cell RNA sequencing analysis.
See also Figures S4–S6 and Table S2.
