Figure 5.
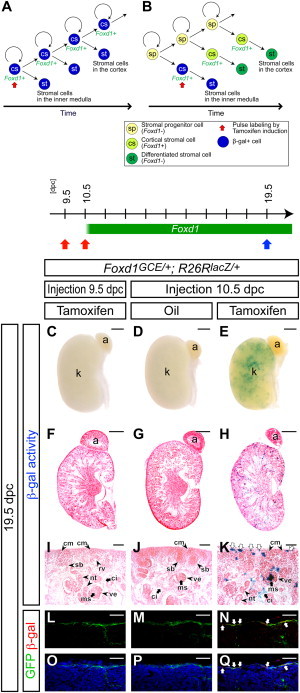
Foxd1+ Cortical Stromal Cells Self-Renew
(A and B) Models for maintenance of cortical stromal cells.
(A) A pulse-labeled β-gal+ (blue) Foxd1+ cortical stromal (cs) cell produces another β-gal+ Foxd1+ cortical stromal cell, which results in retention of β-gal+ cells in the Foxd1+ cortical stroma. Differentiated stromal cells (st) are β-gal+ cells along the cortico-medullary axis throughout kidney organogenesis.
(B) A Foxd1− stromal precursor population (sp) that generates Foxd1+ cortical stromal cells (cs) resides outside of the Foxd1+ population. Contribution of β-gal− cells from the Foxd1− stromal precursor population (sp) dilutes the pulse-labeled β-gal+ (blue) cells in the Foxd1+ cortical stroma (cs; light green). Only differentiated stromal cells (st) at early stages will be β-gal+ (blue) cells that will be seen in the inner medulla (papilla), but stromal cells in the renal cortex (st; dark green), which differentiate at later stages, will be β-gal−.
(C–Q) Foxd1GCE/+; R26RlacZ/+ kidneys at 19.5 dpc after injection of 2 mg tamoxifen at 9.5 dpc (C, F, I, L, and O) and 10.5 dpc (E, H, K, N, and Q), and oil only at 10.5 dpc (D, G, J, M, and P).
(C–E) Whole-mount β-gal-stained (blue) kidneys.
(F–H) Sections of β-gal-stained (blue) kidneys counterstained with eosin (pink).
(I–K) Higher magnification of the cortical region in (F)–(H), respectively. White arrows in (K) indicate multiple β-gal+ cells in the cortical stroma.
(L–Q) Confocal immunofluorescence images with anti-GFP (green), anti-β-gal (red), with (L–N) or without (O–Q) Hoechst (blue) staining. White arrows in (N) and (Q) indicate β-gal+ GFP+ cortical stromal cells.
a, adrenal gland; ci, renal cortical interstitium; cm, cap mesenchyme; k, kidney; ms, mesangium; nt, nephron tubule; pe, parietal epithelium; pr, pericyte; rv, renal vesicle; ve, visceral epithelium (podocyte). Scale bars, 500 μm (C–H) and 50 μm (I–Q).
