Figure 3. Sequence analysis for cDNA and quantitative reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) study for NDRG1.
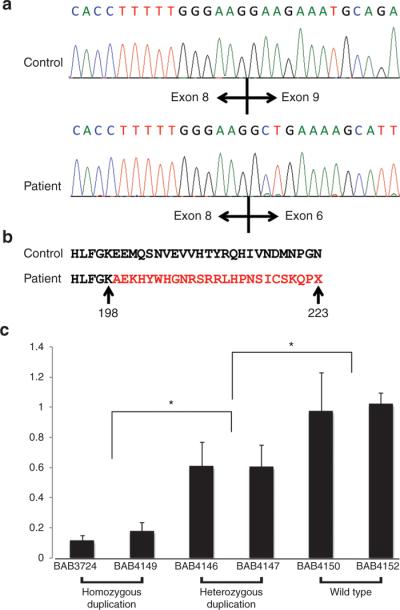
(a) Sanger sequence results of cDNA from the control and affected individuals. In healthy individuals, exon 8 is followed by exon 9 and in affected individuals exon 8 is followed by exon 6. (b) Analysis of the resultant sequence at the amino acid level. The duplication causes a frame shift mutation, altering the amino acid sequence for several residues before a premature termination codon. (c) Expression levels in blood were measured by quantitative RT-PCR using the TaqMan gene expression assay in triplicate and normalized to TBP. We observed a decrease in expression, 0.12- to 0.18-fold in patient samples (BAB3724 and BAB4149) and 0.6- to 0.61-fold in carriers (BAB4146 and BAB4147), compared with normal expression controls. We found an obviously decreased expression in both patients and carriers compared with control healthy individuals. *P < 0.01.
