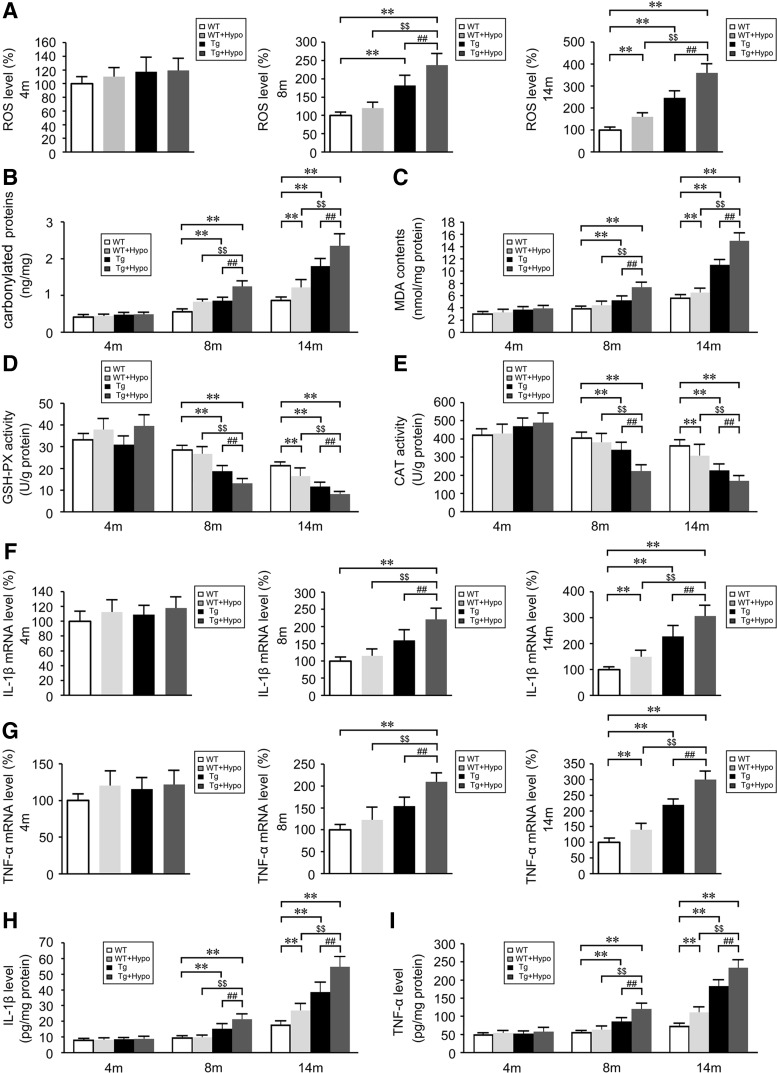
FIG. 3.
Hypoxia increases oxidative stress and inflammatory events in the brain of APP/PS1 and aging WT mice. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels (A), carbonyl proteins (B), and malondialdehyde (MDA) contents (C) in the brains of APP/PS1 transgenic (Tg) and aging WT mice. (D, E) Activities of antioxidant enzymes, glutathione peroxidase (GSH-PX), and catalase (CAT). Relative mRNA expression of interleukin (IL)-1β (F) and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNFα) (G) normalized to β-actin in CD11b+ cells from Tg and age-matched WT brains. ELISA analyses show the levels of IL-1β (H) and TNFα (I). **p<0.01 versus WT group, ##p<0.01 versus Tg group, $$p<0.01 versus WT+Hypo group by repeated-measures ANOVA, n=6–8 in each group. Values represent the mean±SEM.