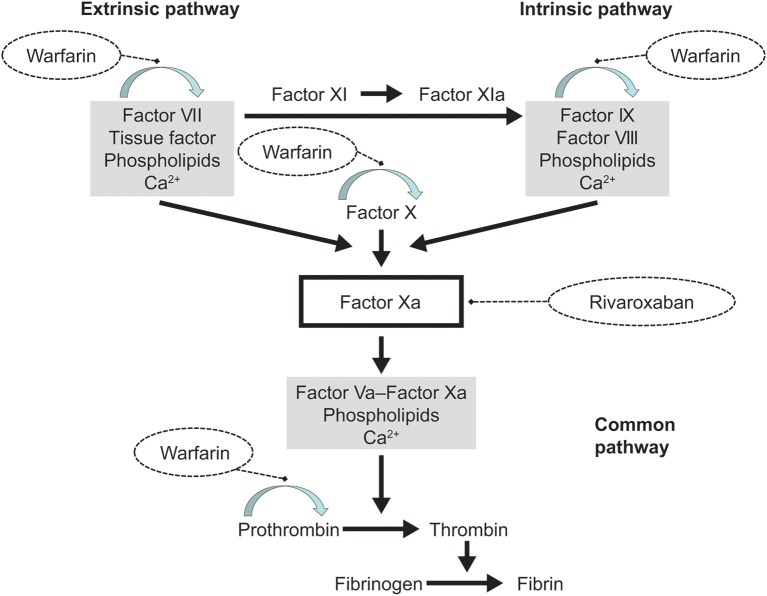
Figure 1.
Overview of the processes accounted for by the coagulation model. The blood coagulation model represents the biochemical reactions that result in factor activation. The extrinsic and intrinsic pathways of the model lead to thrombin and fibrin formation downstream of Factor Xa, known as the common pathway. Drug action is represented by the competitive inhibition of Factor Xa by rivaroxaban and by down-regulation of the vitamin K-dependent synthesis (arched arrow) of the factors VII, IX, and X, and prothrombin (Factor II) by warfarin. These structural elements of the coagulation cascade, as well as proteins C and S (not depicted), formed the basis of the model by Burghaus et al. (2011).