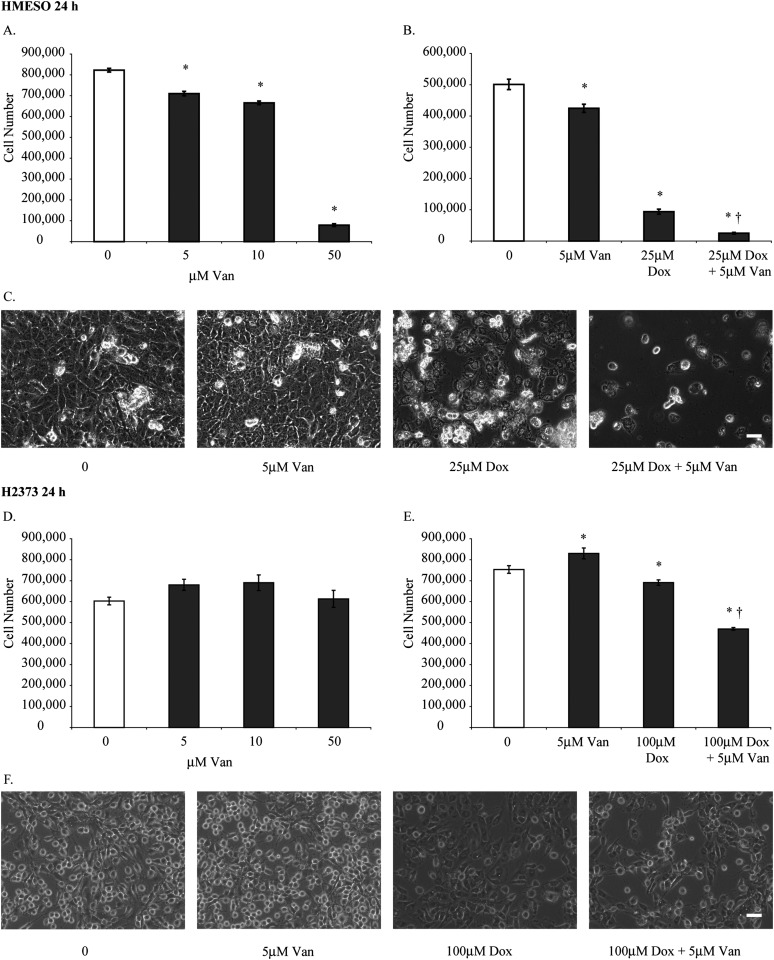
Figure 1.
A combination of doxorubicin (Dox) and vandetanib (Van) is more cytotoxic than either agent alone. (A, D) Two different malignant mesothelioma (MM) cell lines (HMESO and H2373) were treated with 5, 10, and 50 μM Van for 24 hours, and total cell numbers were determined. Results (using both the colorimetric MTS Cell Proliferation Assay and counting of adherent, viable cells at 24 h) of dose-response studies using Dox at a range of concentration from 0.1 to 100 μM concentrations have been previously reported for the HMESO and H2373 (also referred to as PPM Mill) mesothelioma cell lines (11, 37). Based on these results, concentrations of Dox (25 μM for HMESO and 100 μM for the more resistant H2373 line) were selected for studies here. A comparable minimally toxic concentration of Van (5 μM) was used in both lines to demonstrate synergistic effects with Dox based on dose-response data. After exposure to Dox, we used the Apostain assay and LDH assay to show that necrosis and apoptosis occur in a number of MM lines in studies cited above. (B, E) Viability of HMESO and H2373 cells was assessed after treatment with 5 μM Van, 25 μM Dox for HMESO, 100 μM Dox for H2373, or a combination of Dox and Van (25 μM Dox + 5 μM Van for HMESO and 100 μM Dox + 5 μM Van for H2373) for 24 hours. (C, F) Inverted phase microscopy images correlate with total cell numbers in HMESO and H2373 cells after treatment for 24 hours (scale bar = 50 μm). *P ≤ 0.05 as compared with control (0); †P ≤ 0.05 as compared with Dox alone (n = 3 per group/experiment).