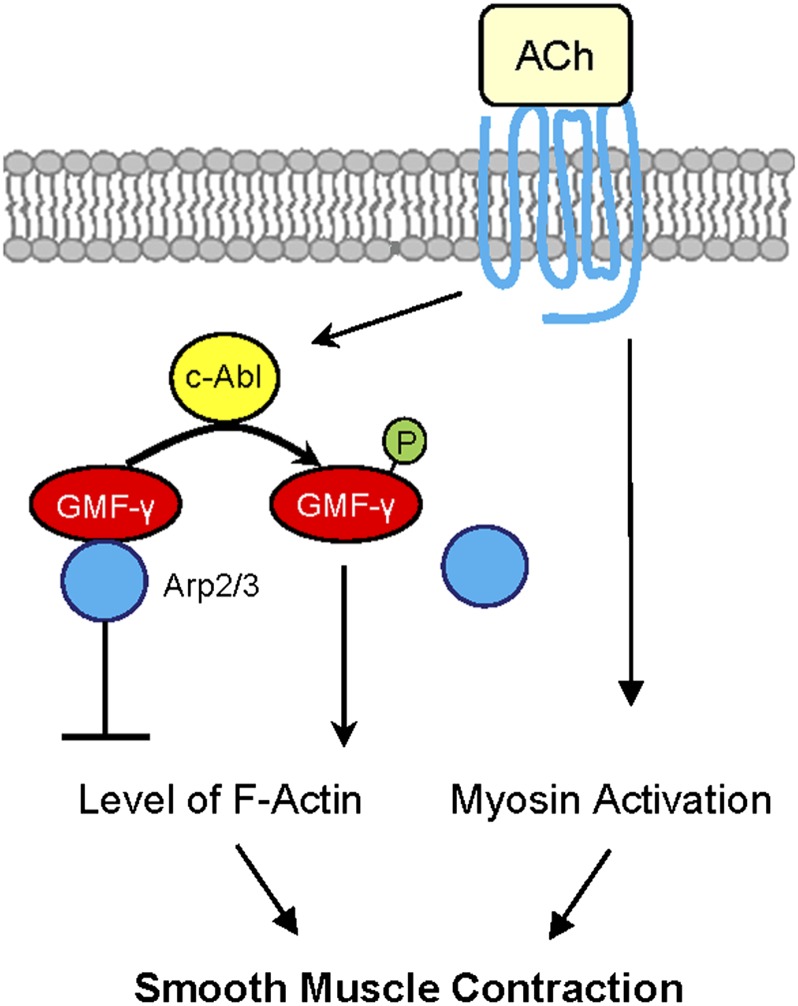
Figure 7.
Proposed mechanism. In unstimulated smooth muscle, GMF-γ functions as an actin network assembly suppressor. GMF-γ binds to Arp2/3, which induces actin disassembly. In addition to myosin activation, agonist stimulation activates c-Abl tyrosine kinase, which catalyzes GMF-γ phosphorylation at Tyr-104. This phosphorylation may induce conformation changes, which leads to the dissociation of GMF-γ from Arp2/3 (disinhibition) and promotes actin network assembly and force development in smooth muscle.