Figure 1.
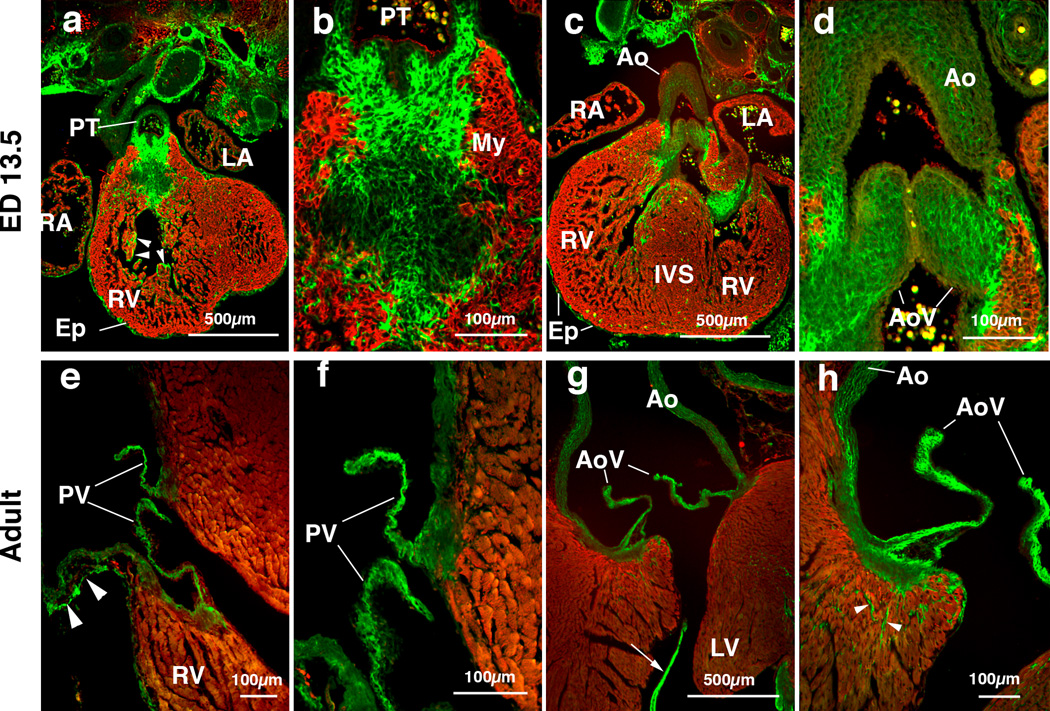
Periostin localization in mouse cardiac outflow tract (OT) and OT valves at embryonic day (ED) 13.5 (panels a-d) and in adult (panels e-h).
(a) Frontal section of an ED 13.5 mouse embryo shows robust expression of periostin (green) in the pulmonary trunk (PT). Epicardium (Ep) and endocardial lining of the ventricular trabeculae (arrow heads) show intense periostin expression. MF20 staining is confined to the myocardium (My, red).
(b) Higher magnification view of the pulmonary trunk mesenchyme in panel a, showing fibrous immunostaining of periostin.
(c) Frontal section of an ED 13.5 mouse embryo shows intense expression of periostin in the forming aortic valves. (d) Higher magnification view of the forming aorta in panel c, showing intense expression of periostin in the aortic valves (AoV) and aortic wall (Ao). Periostin expression within the forming aortic valves seems to be widespread.
(e) Image of an adult mouse heart showing intense periostin immunostaining in the pulmonary valves (PV). Periostin expression is also observed in the pulmonary wall in a loosely organized pattern (arrowheads).
(f) Higher magnification view of (e), showing periostin expression in the pulmonary valve leaflets (PV).
(g) Image of an adult mouse heart showing intense immunostaining of periostin in the aortic valves (AoV). Periostin is also expressed in the tendinous cords of the valve supporting apparatus (arrow).
(h) Higher magnification view of (g), showing intense staining of periostin in the aortic valves and aortic wall. Note that periostin is also localized in MF20-negative non-myocardial cells in the left ventricular wall (arrowheads, green) in the ventricular myocardium. IVS, interventricular septum; LA, left atrium; LV, left ventricle; RA, right atrium; RV, right ventricle.