Fig. 4. Eya4 is restricted to the hair cells in mature neuromasts and ampullary organs.
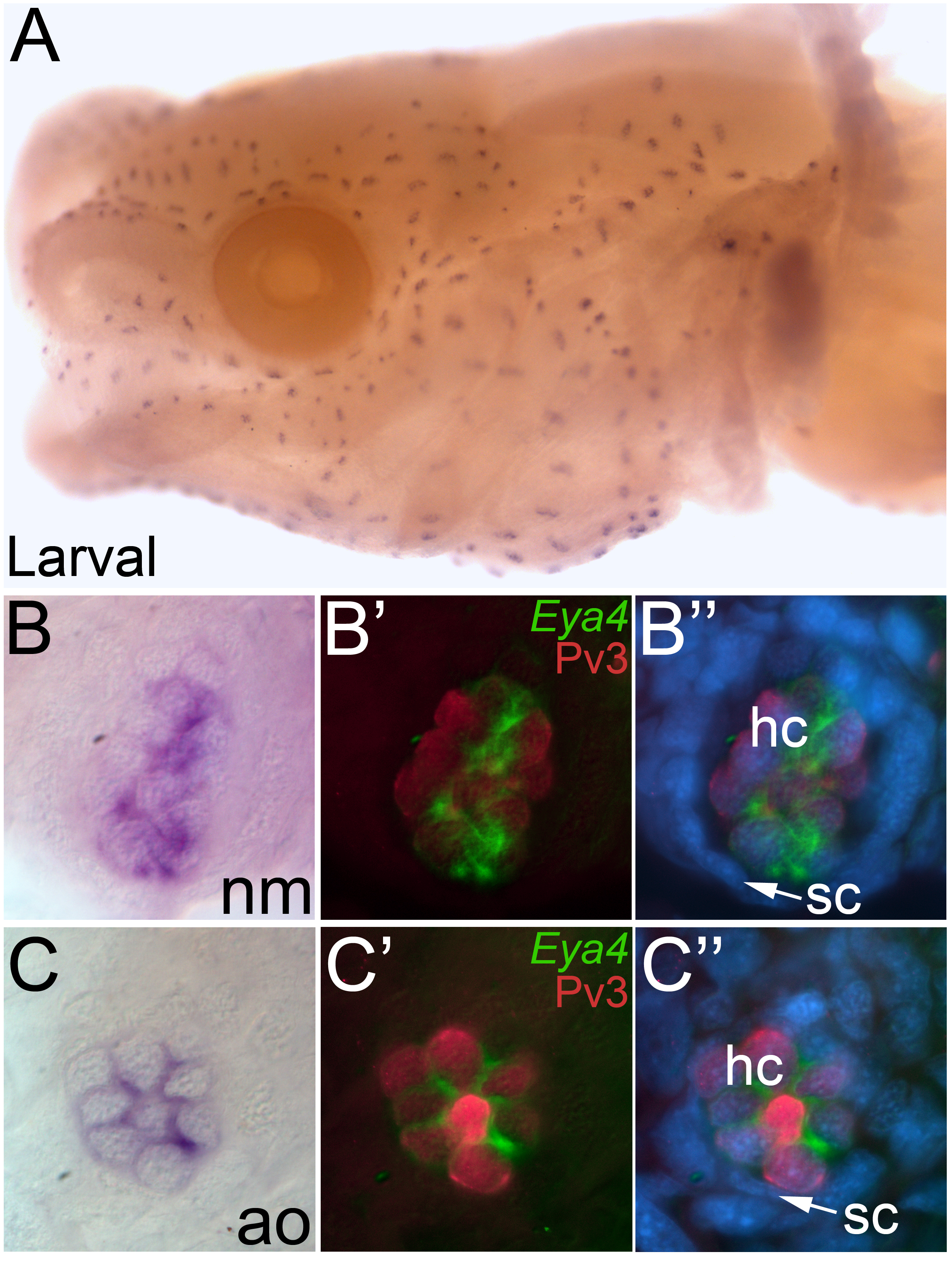
Whole-mount in situ hybridization for Eya4 in larval axolotls. (A) Head view of a larval axolotl. Anterior to the left, lateral view. Eya4 expression is observed in both the neuromasts and ampullary organs. (B) Higher power view of a single neuromast, showing the restricted localization of Eya4. (B’, B”) Fluorescent image of the neuromast in B, immunostained for the hair cell marker Pv3 (red) with Eya4 as a false colored overlay (green) plus (in B”) the nuclear marker DAPI (blue). (C) Higher power view of a single ampullary organ showing the restricted localization of Eya4. (C’, C”) Fluorescent image of the ampullary organ in C, immunostained for the hair cell marker Pv3 (red) with Eya4 as a false colored overlay (green), plus (in C”) the nuclear marker DAPI (blue). In both neuromasts and ampullary organs, Eya4 transcripts are localized within the cytoplasm of the Pv3-positive hair cells. Abbreviations: ao, ampullary organ; hc, hair cell; nm, neuromast; sc, support cell.
