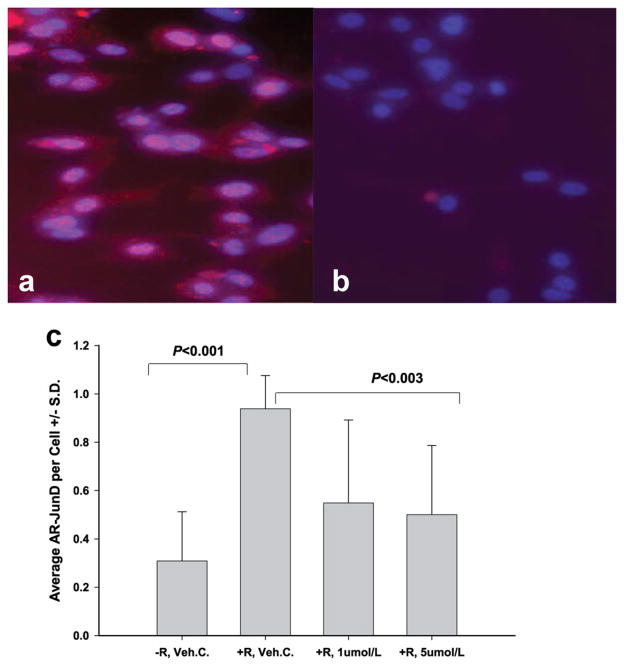
Fig. 4.
Inhibition of androgen-induced AR-JunD interaction by GWARJD10 in LNCaP cells. The DuoLink Proximity Ligation Assay (PLA) technique was used to analyze the effect of lead compound GWARJD10 on androgen-induced AR-JunD interaction. Androgen-dependent LNCaP cells were treated for 72 hr either with 2 nmol/l androgen R1881, positive control (a) or with 2 nmol/l R1881 and 5 μmol/l of GWARJD10 (b). In (a), androgen-induced interactions of AR with JunD are represented by red spots in the cytoplasm and by pink spots in the nuclei which are the merge of red spots with blue DAPI. With the addition of GWARJD10 (b), the interactions of the two proteins were inhibited and few AR-JunD interaction spots were observed (magnification 20×). In (c), LNCaP cells treated with (+) or without (−) 2 nmol/l androgen R1881 (R) and either 0.25% DMSO drug vehicle control (Veh.C.) or 1 or 5 μmol/l GWARJD10 for 72 hr were analyzed by PLA for AR-JunD interaction. Fluorescent spots resulting from AR-JunD interaction (red) were counted and normalized to the number of cells (blue, DAPI) per field using an inverted fluorescent microscope. The three fold induction of AR-JunD interaction by androgen (P <0.001) was significantly reduced by both 1 and 5 μmol/l GWARJD10 (P <0.003). The level of AR-JunD interaction in +R, 5 μmol/L GWARJD10 was not significantly different from androgen-deprived control −R, Veh. C.N = 12 fields counted percondition across two experiments(6 fields per experiment).