Figure 2.
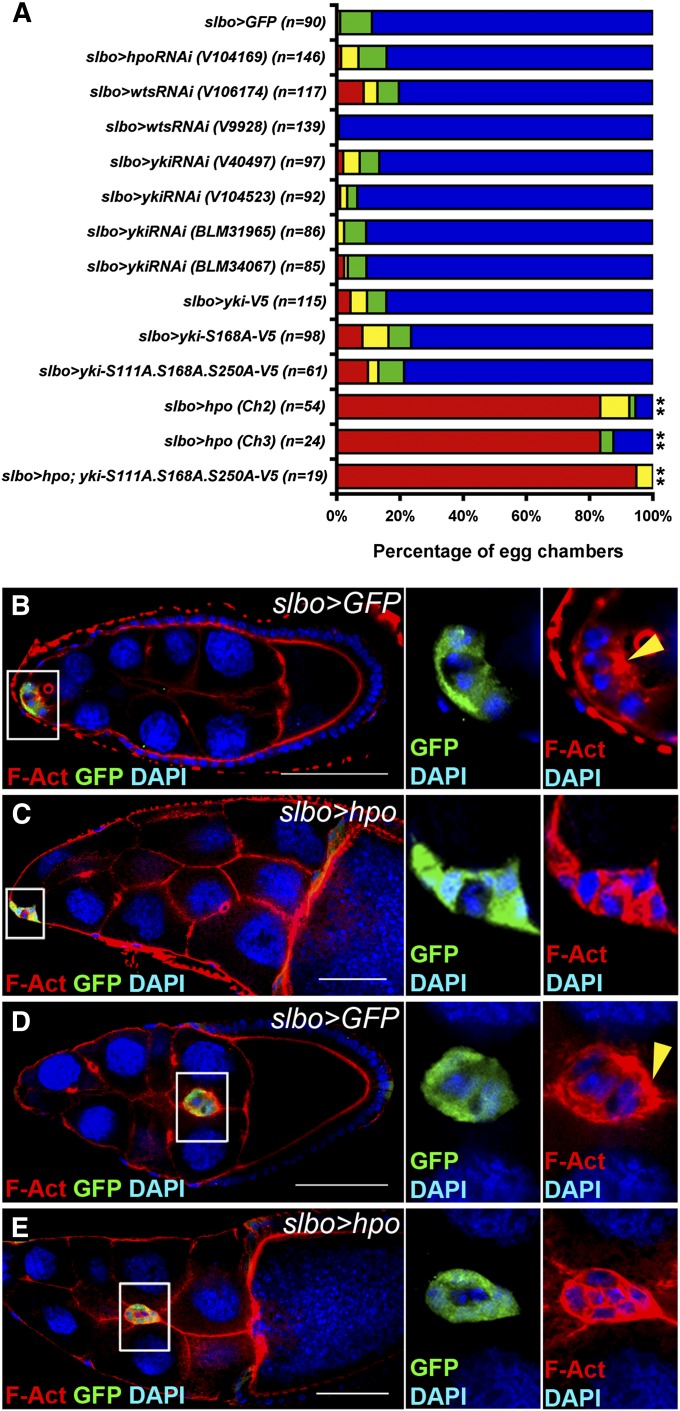
Overexpression of hpo with slbo-Gal4 increases filamentous actin between border cells and disrupts border cell migration. slbo-Gal4 was used to overexpress or knock down genes specifically in outer border cells. UAS-GFP driven by slbo-Gal4 was used as a control. The flies were dissected after being grown at 29° for 6 days. (A) Stage-10 egg chambers were selected for quantification. Colors of the graph represent the migratory distance depicted in Figure 1I. Numbers of egg chambers examined are indicated. Inhibition of hpo, wts, or yki in outer border cells did not affect border cell migration in comparison with that in the control. Overexpression of yki or constitutively active forms of yki, yki-S168A, and yki-S111A.S168A.S250A with slbo-Gal4 driver did not affect border cell migration. Overexpression of hpo with two different UAS-hpo lines severely disrupted border cell migration. The migratory defect was not alleviated when yki-S111A.S168A.S250A were overexpressed. Wilcoxon rank-sum test, **P < 0.01. (B–E) The ovaries were stained with anti-GFP, DAPI, and phalloidin for filamentous actin (F-actin). Border cell clusters were delaminating from the follicular epithelium (B and C) or migrating toward the oocyte (D and E). High magnification of border cell clusters is shown on the right. (B) In the UAS-GFP control, F-actin was enriched in the apical region of a border cell cluster indicated by a yellow arrowhead. (C) When hpo was overexpressed, F-actin was enriched between border cells. (D) In the UAS-GFP control, F-actin was enriched in the outer rim, especially in the front edge, of a migrating border cell cluster indicated by a yellow arrowhead. (E) When hpo was overexpressed, F-actin was enriched in boundaries between border cells as well as the outer rim. Bar, 20 μm in B–E.