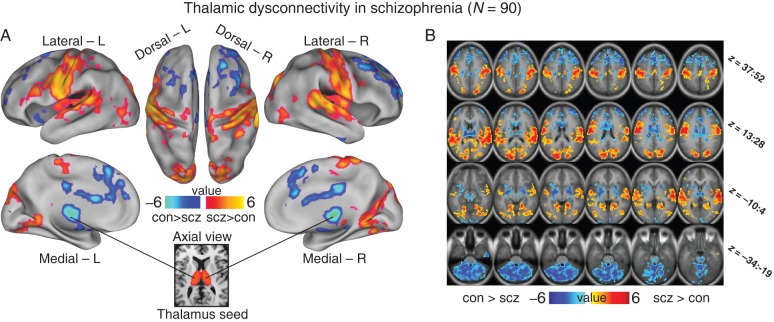
Figure 1.
Thalamic dysconnectivity in schizophrenia. (A) Significant whole-brain between-group differences in thalamic connectivity between healthy controls (CON) and individuals with schizophrenia (SCZ). Red-orange foci mark areas where patients exhibited stronger thalamic coupling; blue foci mark areas where patients exhibited reduced thalamic coupling relative to healthy controls (Supplementary Tables 1 and 2 list all foci showing significant between-group differences). The bottom inset illustrates a thalamic seed. (B) Volume-based axial view with Z-coordinate ranges (each slice in each row increments by 3 mm). For group-specific unthresholded connectivity patterns see Supplementary Figure 1; and for comprehensive between-group contrasts across samples see Supplementary Figures 2 and 4. For a formal conjunction analysis with a priori-defined sensory–motor networks see Supplementary Figure 12.