Figure 2.
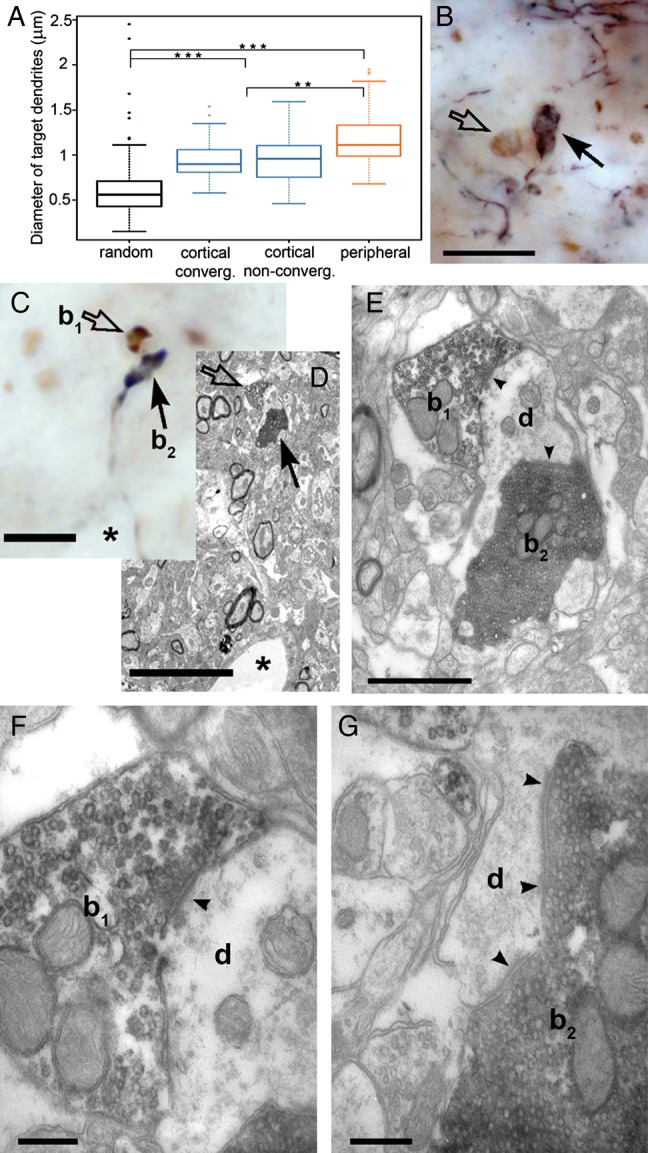
Convergence of cortical and brainstem driver terminals on a single dendrite. (A) Whisker plots showing the minor diameter of randomly selected dendrites compared with those postsynaptic to large cortical (in convergent and nonconvergent zones) and subcortical terminals in the rat POm. Both subcortical and cortical drivers innervate large caliber dendrites, which are significantly thicker than the diameter of randomly selected dendrites. (B and C) A high-power light micrographs of anterogradely labeled large cortical terminals (arrows) and vGluT2-positive subcortical terminals (open arrows) apparently facing a single postsynaptic target in the neuropil of mouse (B) and rat (C). (D) Correlated low-power electron microscopic image of the terminals shown in C. A capillary (asterisk) serves as a landmark. (E) Electron microscopic images demonstrating that both terminals (subcortical b1, cortical, b2) converge and establish synapses (arrowheads) on the same dendrite (d). (F) High-power image of the vGLUT2-positive terminals showing the synaptic cleft (arrowhead) and the presynaptic vesicle accumulation. (G) High-power image of the cortical terminal showing additional synapses (arrowheads) on the same target, a characteristic feature of driver terminals. Scale bar, B, C, D: 10 μm; E: 1 μm; F–G: 250 nm.
