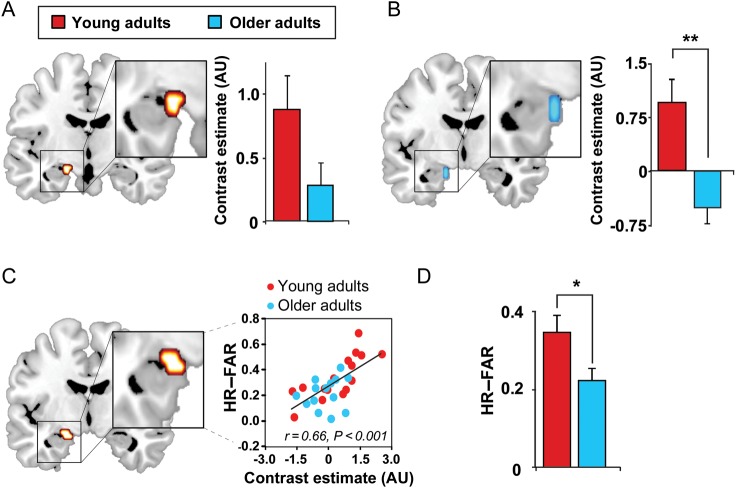
Figure 2.
Effects of age on hippocampal functioning. (A) Hippocampal activation greater during successful associative episodic encoding than unsuccessful associative encoding (Hits–Lures; 8-mm sphere ROI: x = −21, y = −6, z = −15) (Miller et al. 2008) and (B) corresponding age effects (Hits–Lures; older < young adults) in the same ROI. (C) Regression between episodic learning and encoding-related hippocampal activation (Hits–Lures) in the above-mentioned ROI. (D) Episodic learning in young and older adults, both performing significantly greater than chance (HR-FAR: hit rate to originally studied faces–false alarm rate to new, unstudied faces). Activations are displayed and considered significant at the voxel level of P < 0.05 FWE, corrected for multiple comparisons within the a priori hippocampal ROIs (Miller et al. 2008). Hot colors represent the extent of activation in both young and older adults, and cold colors represent the extent of decreased activation in older, relative to younger, adults. While the 8-mm sphere ROI used to correct for multiple comparisons did extend outside the hippocampus, no effects were detected or presented outside the hippocampus in the current report. Bilateral effects were detected in the hippocampus, when using an anatomical hippocampal mask, albeit at a lower statistical threshold (P < 0.005 uncorrected; Supplementary Fig. 2). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.001.