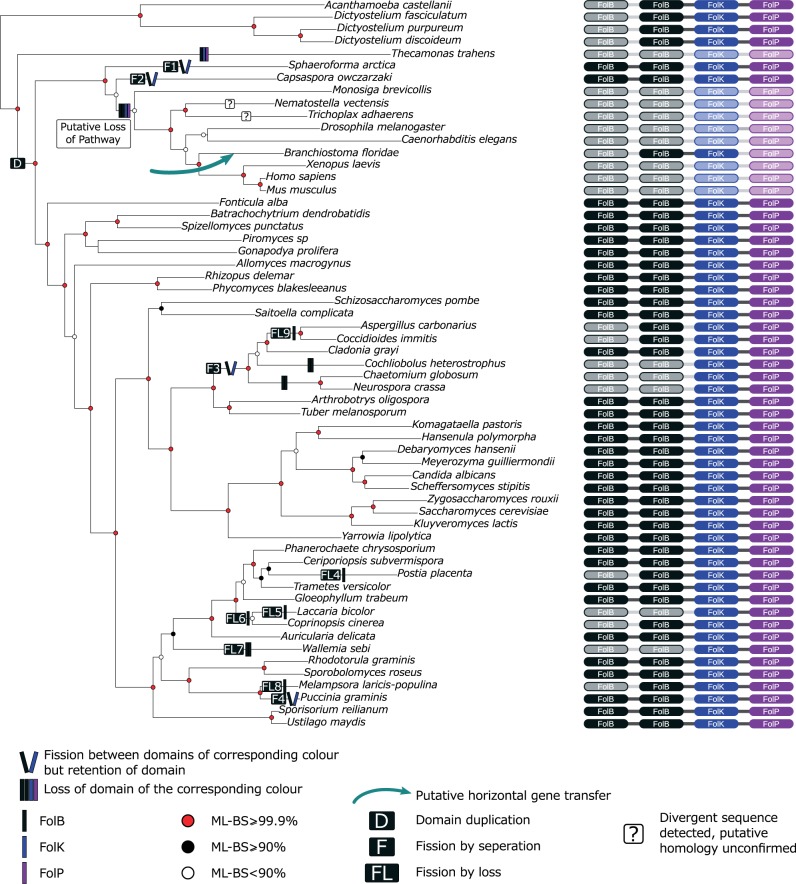
Fig. 3.—
Phylogeny of the Apusomonadida, Breviata, Opisthokonta, and Amoebozoa demonstrating variation in the folB-folK-folP fusion gene. Tree topology was calculated using a concatenated alignment of conserved genes identified in (Torruella et al. 2012) and represents the best-known likelihood tree from 100 ML searches in RAxML (PROTCAT+LG) with 1,000 nonrapid bootstraps. ML-BS is an abbreviation of maximum likelihood bootstrap values, FolB-folK-folP fusion gene domain architecture of taxa included is listed down the right column, and fusion state is denoted by the presence/absence of connecting lines. Inferred gene/domain losses are shown as shadow domains. See key for guide to tree topology support values and character state changes. Domain duplication is indicated as (D) in a box of the appropriate domain colour, fission by domain loss events are denoted as (FL5–9) and specific fission events as (F1–4). Total losses of complete ORFs are not illustrated. Note that the putative folB of Trichoplax adhaerens and the putative folB-folK fusion of Nematostella vectensis were removed from phylogenetic analyses due to poor alignment of these sequences, as such their provenance and evolutionary ancestry remains questionable and are therefore indicated by a question mark at the relevant position.