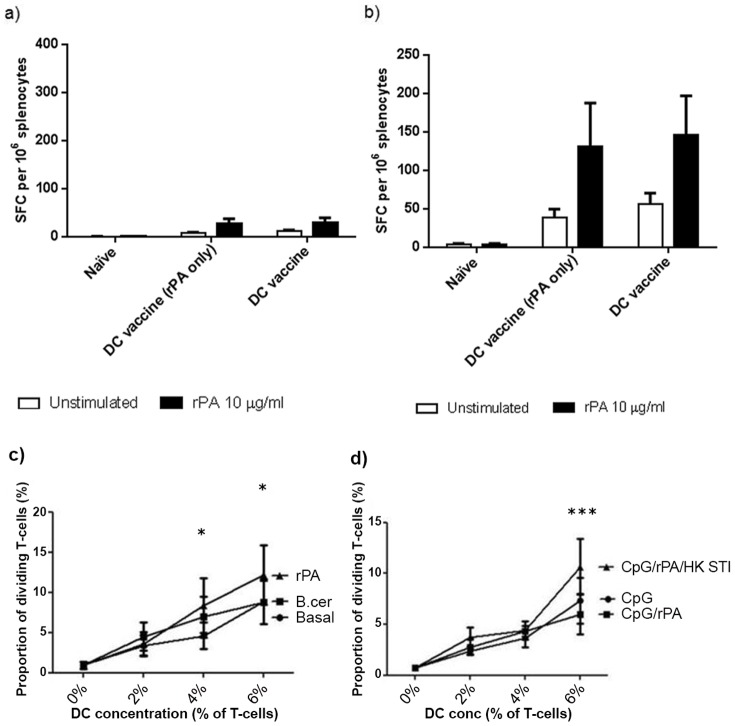
Figure 2. Stimulation of T cell responses.
a and b) DCs were stimulated with rPA only (DC vaccine rPA only) or with PA, heat killed B. anthracis and CpG oligonucleotides (DC vaccine) and administered i.d. to A/J mice. Spleens were taken at 7 days (a) and 14 days (b) post- vaccination and restimulated ex vivo with rPA. A one-way Anova with Tukey multiple comparison post-hoc test was performed on the results (* p<0.05, ** p<0.01, *** p<0.001). Error bars represent the standard error of the mean calculated from the means of three replicates from five animals. c) Proliferation of CD4+ naive human T cells following 5-day co-culture with syngeneic human DC pulsed with medium only, B. cereus or rPA (n = 5). After 2-way ANOVA analysis with Bonferroni corrections, there were no significant differences between B. cereus and medium only (basal)-pulsed DC regarding stimulatory capacity but rPA-pulsed DC were significantly more stimulatory than basal conditions at 4% and 6% (p<0.05 in both cases) and significantly more stimulatory than B. cereus pulsed DC at 6% (p<0.05). d) CD4+ naive human T-cell proliferation following 5-day co-culture with syngeneic DC pulsed with CpG only, rPA with CpG or combination of rPA, CpG and HK B. anthracis (n = 3). After 2-way ANOVA with Bonferroni corrections, there were no significant differences between CpG and rPA/CpG-pulsed human DC regarding stimulatory capacity but rPA/CpG/HK B. anthracis-pulsed human DC were significantly more stimulatory than both other conditions at 6% (p<0.001 in both cases).