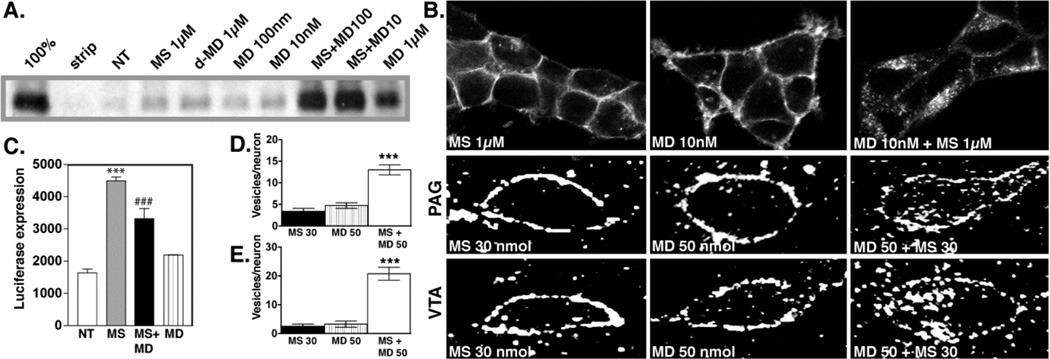
Figure 13. Trafficking of the MOR with morphine and the cocktail.
A. Biotin protection assay to quantify endocytosis. HEK293 cells stably expressing FLAG-tagged MORs were examined for endocytosis by biotin protection. Methadone enhanced morphine-induced endocytosis. Saturating concentrations of morphine alone (1 µM) or d-methadone (1 µM), as well as low concentrations of dl-methadone (100 nM, 10 nM) failed to promote endocytosis. A saturating concentration (1µM) of dl-methadone alone promotes endocytosis. B. Immunocytochemical staining. HEK293 cells stably expressing FLAG-tagged MORs receptors were fed antibody, exposed to 1µM morphine, 10nM methadone or both then fixed and stained for receptor. Methadone enhanced morphine-induced MOR endocytosis. C. cAMP superactivation. CRE-luciferase expression was assessed in HEK293 cells stably expressing both the MOR and a CRE-luciferase reporter gene. Cells were treated with drug or drug combinations for 14 hrs, washed then treated with 2 µM forskolin for 4 hrs. Morphine induced cAMP superactivation, while methadone decreased morphine-induced cAMP superactivation (***p<.001 NT vs. MS, ###p<.001 MS vs. MS+MD, 1xANOVA, Tukey post-test.) MD; dl-methadone, MS morphine sulfate, NT no treatment. D, E. Immunohistochemistry in rat brain. MOR distribution in PAG (D) and VTA (E) neurons was assessed 30 mins after acute i.c.v. administration of drug. Neither methadone (50 nmol) nor morphine (30 nmol) promoted endocytosis of the MOR, while co-administration of both induced MOR endocytosis. For quantification, slides were encoded and vesicles counted by a second party blind to treatment. (***p<.001: MS 30 nmol+ MD 50 nmol vs. MS 30 nmol or MD 50 nmol). Reproduced with permission from He, L., Whistler, J.L., 2005. An opiate cocktail that reduces morphine tolerance and dependence. Curr. Biol. 15, 1028–1033.