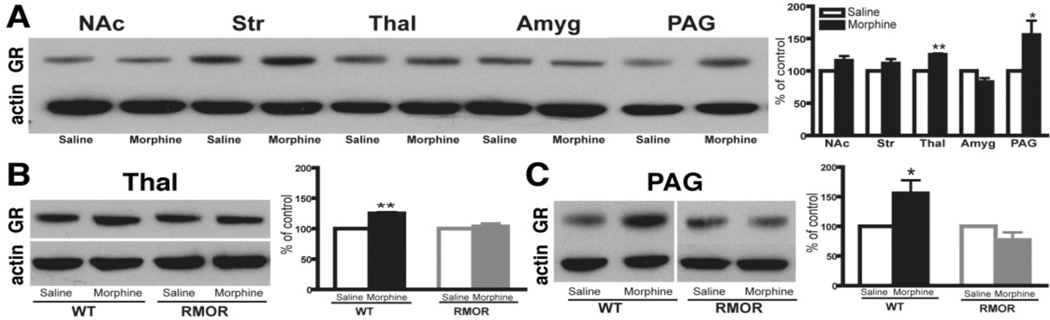
Figure 7. Effects of chronic morphine treatment on GR levels.
A. Chronic morphine induced a significant increase in GR immunoreactivity in the thalamus and PAG of WT mice. B, C. Chronic morphine caused no change in RMOR mice in either thalamus (B) or PAG (C). In all cases, data are expressed as mean ± SEM of at least three separate experiments. NAc: nucleus accumbens; Str: striatum; Thal: thalamus; Amyg: amygdala; PAG: periaqueductal gray. * p< 0.05, ** p < 0.01, compared with saline group. Reproduced with permission from He, L., Kim, J.A., Whistler, J.L., 2009. Biomarkers of morphine tolerance and dependence are prevented by morphine-induced endocytosis of a mutant {micro}-opioid receptor. Faseb J. 23, 4327–4334.