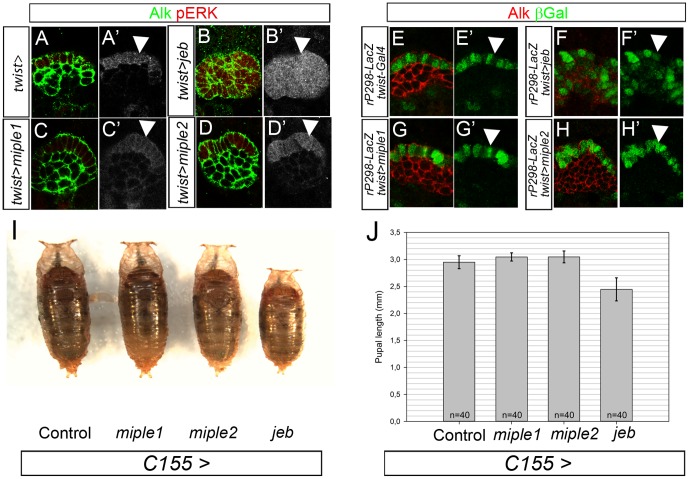
Figure 3. Ectopic expression of Miple proteins does not activate Alk signaling.
(A-D) Ectopic expression of Miple1 (C, C′) or Miple2 (D, D′) with twist2xPE-Gal4 in stage 10 embryos fails to ectopically activate ERK (pERK) in Alk positive visceral mesoderm. This is in contrast to ectopic expression of Jeb which is sufficient to activate ERK (pERK) in all Alk positive cells of the visceral mesoderm (B′ compare with C′ and D′, arrowhead). (E-H) Ectopic expression of Miple1 (G, G′) or Miple2 (H, H′) with twist2xPE-Gal4 fails to ectopically activate the duf/kirre enhancer trap rP298-LacZ. As observed with pERK above (B′), Jeb is sufficient to activate robust LacZ reporter expression in all Alk positive cells of the visceral mesoderm (F′ compare with G′ and H′, arrowhead). (I-J) Ectopic expression of Miple proteins does not affect pupal size during development. Expression of Jeb with the pan-neuronal driver (C155-Gal4) results in a reduction of pupal length (mm) in comparison to controls. In contrast, pan-neuronal expression of Miple1 or Miple2 does not affect pupal size. Representative pupae are shown in (I). Quantification is shown in (J), error bars denote S.E.M. (n = 40). All pupae analysed were female, confirmed by analysis of hatched adults.