Figure 8.
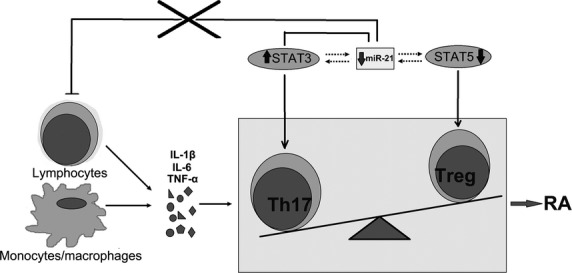
Schematic diagram showing the hypothetical role of miR-21 in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients. In the normal setting, miR-21 can inhibit inflammation by positively regulating Treg cell development or negatively regulating STAT3. However, decreased levels of miR-21 may increase the expression and activation of STAT3, and simultaneously reduce the expression and activation of STAT5, promoting the Th17 cell differentiation while suppressing Treg cell development during chronic inflammation in RA.
