Figure 6.
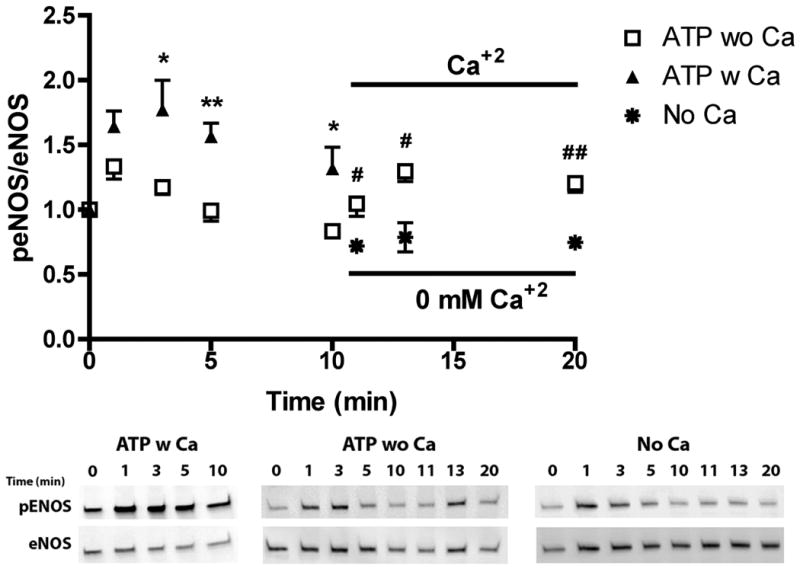
ATP induced eNOS phosphorylation is dependent on the calcium influx from the extracellular space. Cells were simulated with 100 μM ATP in the presence (ATP w CA) or absence of extracellular calcium (ATP wo Ca). Cells were harvested before stimulation (t=0) and at time points 1, 3, 5, and 10 min after stimulation. All peNOS/eNOS ratios were normalized by t=0. eNOS phosphorylation remained elevated after 1 min, which was not seen in the absence of extraceullular calcium. After the initial response to stimulation in the absence of calcium, PBS with calcium was added (t=10) which caused an increase in eNOS phosphorylation that was not observed when PBS without calcium was added. (p<0.05 *,#; p<0.01 **, ## two-tailed t-test; ATP wo Ca+2 n=5, ATP w Ca+2 n=4, addition of PBS with Ca+2 n=3, No Ca n=3)
