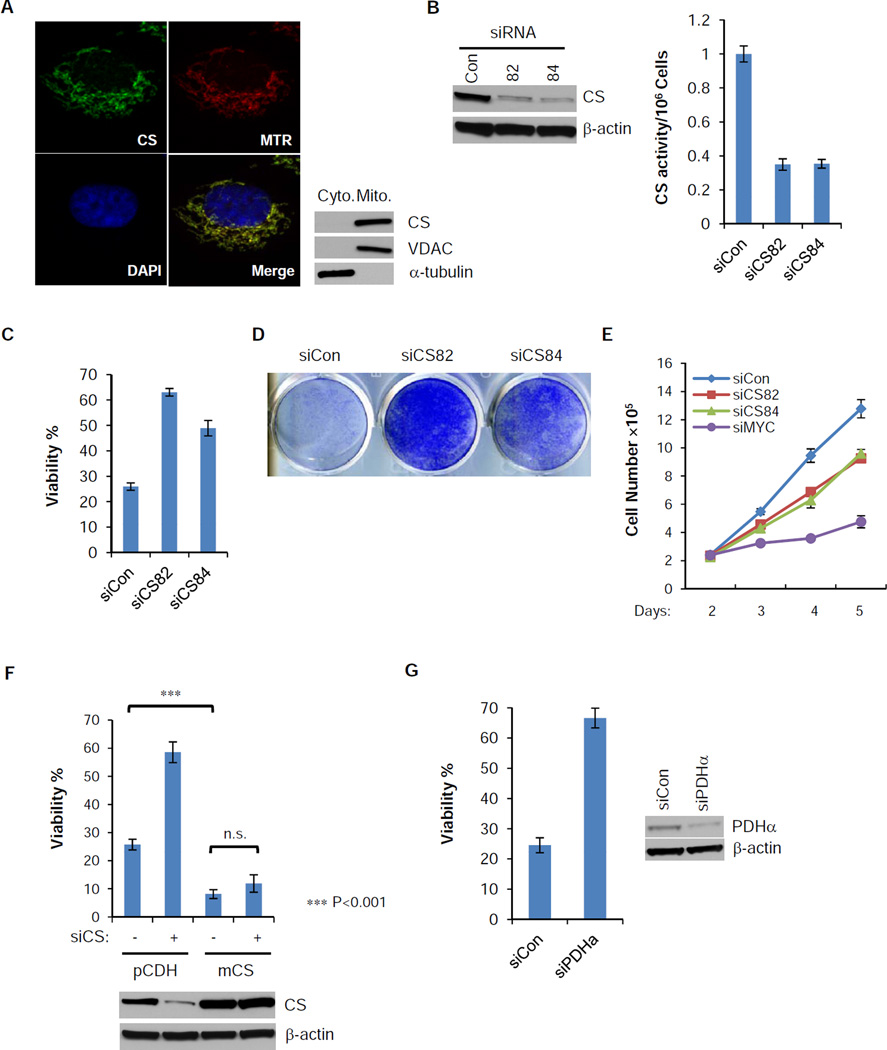
Figure 3. Loss of function of CS protects cells from glutamine withdrawal-induced apoptosis.
(A) SF188 cells were stained with mitoTracker Red (Red), and then fixed and stained with antibody against CS (Green). DAPI (Blue) was applied for nuclear staining. Cytosolic and heavy membrane fractions of SF188 cells were isolated. Distribution of CS was confirmed by western blotting, with VDAC and α-tubulin as mitochondrial and cytosolic markers.
(B) siRNA suppression of CS for 48 hours in SF188 cells reduces both the protein level and the enzymatic activity.
(C,D) SF188 cells were transfected with control or CS siRNA for 2 days and glutamine was deprived for another 48 hours. Viability was measured by Annexin V & PI staining. Crystal violet staining was used to measure total viable cells after 4 days of glutamine depletion followed by re-addition of glutamine for an additional 2 days.
(E) SF188 cells were transfected with control, CS or MYC siRNA in DMEM medium with glutamine, cell numbers were recorded from day 2 to 5 post-transfection.
(F) SF188 cells with constitutively expressed mouse CS (mCS) or empty vector (pCDH) were transfected with control or human CS siRNA for 2 days, and then deprived of glutamine for 48 hours. Viability was measured by Annexin V and PI staining, and expression of total CS was measured by western blotting. p-value was determined by using Student’s 2-tailed t-test.
(G) SF188 cells were transfected with control or pyruvate dehydrogenase subunit α (PDHα) siRNA for 2 days, and then deprived of glutamine for 48 hours. Viability was measured by Annexin V and PI staining.
The data in Figure 3 (B, C, E, F and G) are shown as mean +/− S.D., n=3. See also Figure S2.