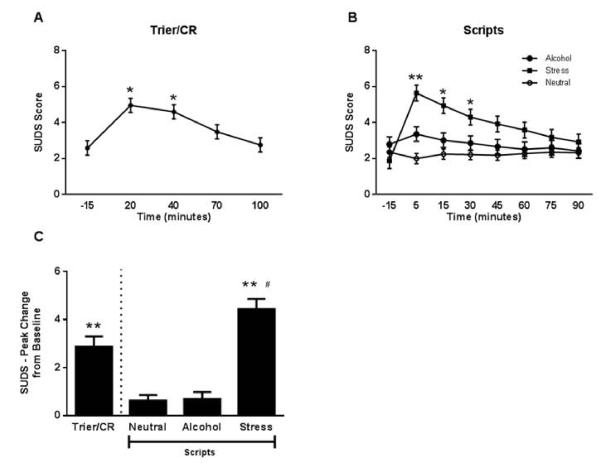
Figure 4.
Subjective stress response to the Trier/CR and scripts.
(A) Time course of the subjective stress response during the Trier/CR (* = different from −15, 70, and 100 minutes; Tukey HSD p < 0.05). Model covariates included gender, treatment, age, number of heavy drinking days, and neuroticism score (n = 50 due to missing data for some of the covariates). (B) Time course of the subjective stress response during the Scripts (** = different from both alcohol and neutral, * = stress different from neutral; Tukey HSD p < 0.05). Model covariates included gender, treatment, age, ADS score, and neuroticism score (n = 50 due to missing data for some of the covariates). (C) Comparison of peak change from baseline stress rating between the Trier/CR and Scripts (** = different from both alcohol and neutral script, # = different from Trier/CR; Tukey HSD p < 0.05). Model covariates included gender, treatment, and CTQ score (n = 50 due to missing data for some of the stress rating rating times, such that the peak change could not be calculated for all subjects). Error bars denote SEM.