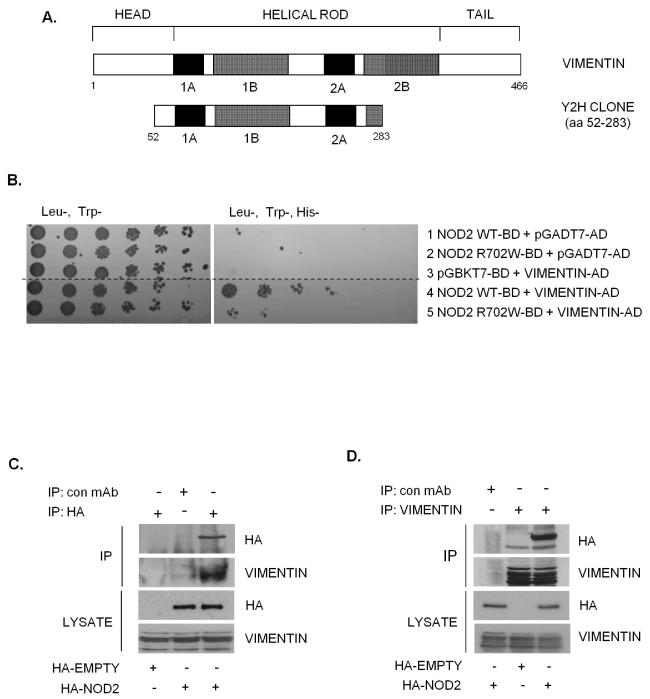
Figure 1. Identification of vimentin as a NOD2 interacting protein.
(a) Schematic showing the structure of vimentin and the vimentin clone identified as binding to NOD2 in our yeast-two-hybrid assay.
(b) Yeast strain AH109 was co-transformed with a plasmid containing the yeast expression vector pGADT7-AD, full-length vimentin cDNA, wild-type NOD2 or CD-associated variant NOD2-R702W as shown. Co-transformants were selected on (Leu-Trp-) plates and spotted onto selective media (His-Leu-Trp-). (Dashed line indicates where irrelevant lanes have been removed).
(c) SW480 cells were transfected with HA-NOD2 or HA-empty vector and extracts immunoprecipitated with HA-11 specific antibodies or non-specific antibody as control. Precipitates were immunoblotted for associated vimentin and NOD2, and direct lysates with HA-11 and vimentin antibodies.
(d) SW480 cells were transfected with HA-NOD2 or HA-empty vector and cell extracts immunoprecipitated with vimentin specific antibodies or non-specific antibody as control. Precipitates were immunoblotted for associated NOD2 and vimentin, and direct lysates with HA-11 and vimentin antibodies.