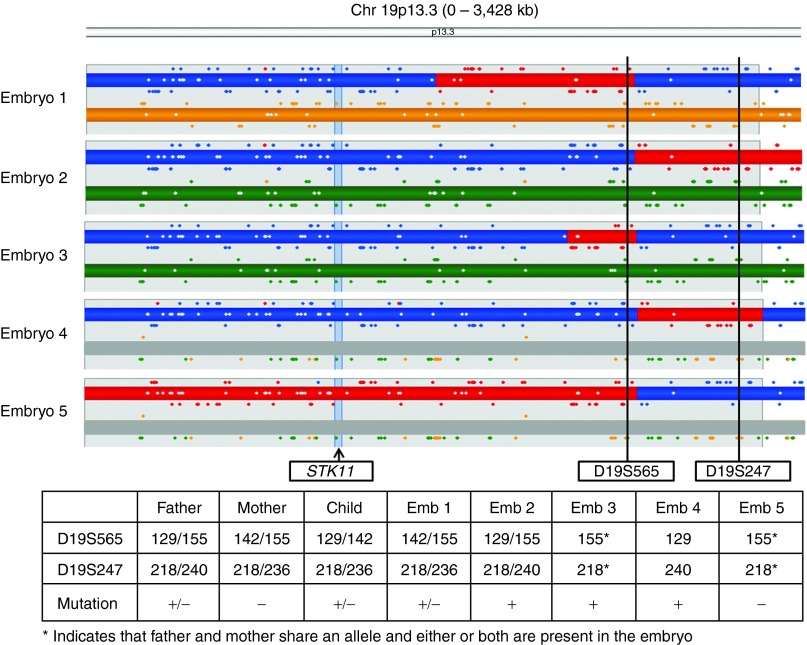
Figure 2.
Detailed karyomaps of chromosome 19, in the terminal p13.3 region, for five embryos from a preimplantation genetic diagnosis case for Peutz–Jeghers syndrome, caused by a mutation in the STK11 gene. Also shown is the outcome of conventional testing with two proximal semi-informative STR markers (D19S565 and D19S247) and direct mutation detection. Paternal haplotypes are represented in blue/red, and maternal haplotypes are represented in orange/green. Haplotypes inherited by the reference are shown in blue/orange. The affected child has inherited the mutation in STK11 from the father. Therefore, the reference haplotype (blue) represents the affected haplotype in this case. Note that there is a common crossover on the paternal chromosome between the two STR markers, which indicates that the affected child used as a reference for linkage had a crossover in this position. Furthermore, there are three additional crossovers in the region on the paternal chromosomes in these five embryos and the maternal chromosome 19 is not present in two embryos (haploblock bar grayed out). This complex pattern of crossovers and aneuploidy detected by karyomapping is completely concordant with the STR alleles (table below) and the presence or absence of the mutation (indicated by the + or − in the STR table). However, Embryos 2, 3, and 4 have identical STR results, and only direct mutation testing identifies Embryo 3 as affected. STR, short tandem repeat.