Figure 1. Selecting peptide structures and RD1 library design.
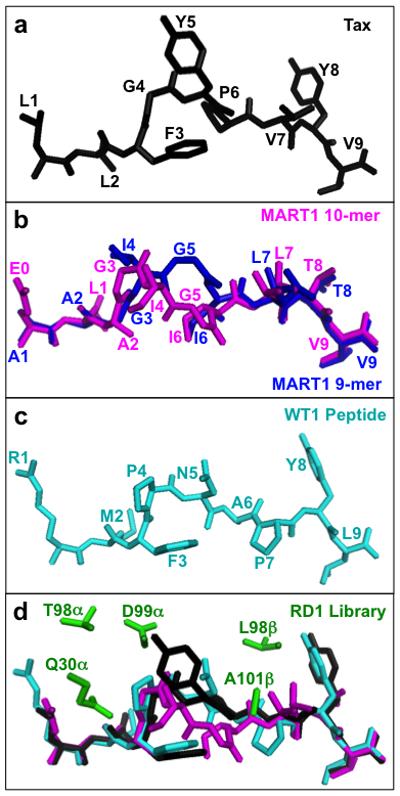
(a) Structure of the HLA-A2-bound Tax peptide (LLFGYPVYV)(PDB: 1DUZ)66, black. (b) Structural alignment of the HLA-A2-bound, decamer MART1 peptide (ELAGIGILTV)(PDB: 1JF1)67, magenta, and the HLA-A2-bound nonamer MART1 peptide (PDB: 2GUO)39, blue. (c) Structure of the HLA-A2-bound WT1 peptide (RMFPNAPYL)(PDB: 3HPJ)68, cyan. (d) Five residues (green), Q30α, T98α, D99α, L98β, and A101β (G in the wild-type A6), generated as degenerate codons in the RD1 library, as found in the structure of the A6-c134:Tax/HLA-A2 complex (PDB: 4FTV)47. A6-c134 contains the same CDR sequences as the single-chain A6-X1534 that was used as the RD1 library template. Tax peptide is in black, MART1 decamer peptide from the aligned Mel5:MART1/HLA-A2 structure (PDB: 3HG1)7 is in magenta, and WT1 peptide from the aligned WT1/HLA-A2 structure (PDB: 3HPJ)68 is in cyan.
