Fig. 1.
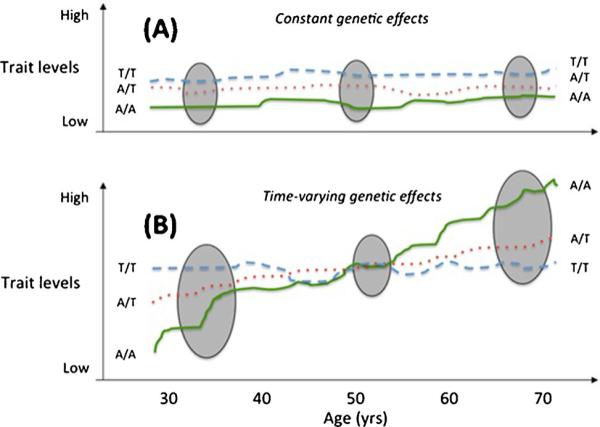
Hypothetical genetic effects that are either constant (Panel A) or time-varying (Panel B). The grey ellipses are sampling occasions for cross-sectional studies. Cross-sectional studies are most likely to detect loci with constant effects, as the sampling time (age) has no impact on genetic effects. By contrast, time-varying genetic effects may be undetectable in a cross-sectional analysis if the age-range of the participating cohorts is broad, or if the sampling occasion is at the cross-over point. Moreover, cross-sectional studies in younger adults would conclude that genotype A/A is protective, even though the genotype conveys high risk later in life
