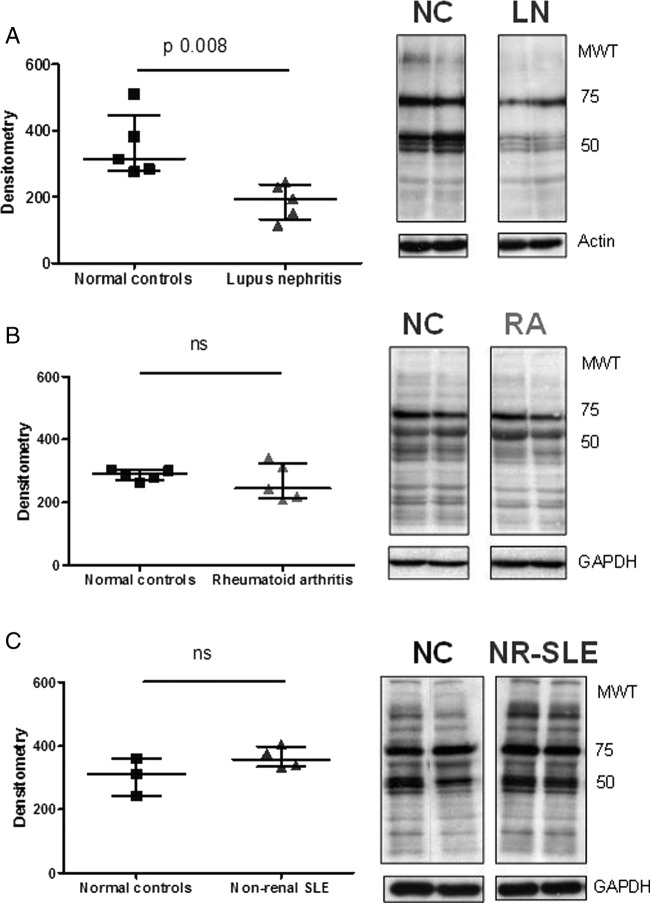
Figure 3.
Comparison of the effects of growing podocytes in plasma from patients with lupus nephritis (LN), rheumatoid arthritis or non-renal lupus. Representative antiphosphotyrosine blots from experiments comparing the effect of growing podocytes for 24 h in normal control (NC) plasma versus plasma from patients with LN (A), rheumatoid arthritis (RA, B) or non-renal systemic lupus erythematosus (NR-SLE, C). Cells were lysed and protein tyrosine phosphorylation assessed by western blot. The graphs display densitometry, with the median and IQR for each group. Medians were compared using the Mann–Whitney test. As already shown, LN plasma leads to a reduction in protein tyrosine phosphorylation, whereas the effect of plasma from patients with RA or NR-SLE is no different to NC. Equal loading was ensured by blotting for either actin or GAPDH.