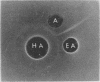
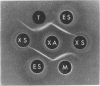
Abstract
Immunoglobulin A (IgA) was demonstrated in equine serum and secretions. This immunoglobulin had a molecular weight extending from 150,000 to 700,000 and reacted with specific antihuman alpha-chain antiserum. Antigenic determinants specific for secretory IgA were demonstrated and found to be absent on serum IgA. Antigen binding activity was detected in IgA from tears. Purified IgA was antigenically distinct from equine IgG, IgM, IgG(T), and aggregating immunoglobulin. Quantitative studies demonstrated that IgA was the predominant immunoglobulin in tears and milk but not in colostrum. The electrophoretic mobility, size, presence of secretory component, and reaction with specific antihuman alpha-chain antiserum demonstrates that this immunoglobulin is the equine homologue of human IgA.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews P. Estimation of the molecular weights of proteins by Sephadex gel-filtration. Biochem J. 1964 May;91(2):222–233. doi: 10.1042/bj0910222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Audibert F., Sandor G. Nature de la fraction antitoxine des immunsérums de cheval. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1968 Jul 22;267(4):457–458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genco R. J., Yecies L., Karush F. The immunoglobulins of equine colostrum and parotid fluid. J Immunol. 1969 Sep;103(3):437–444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helms C. M., Allen P. Z. Studies on equine immunoglobulins. II. Anigenic interrelationships among horse IgG(T) and antipneumococcal gamma-1-component. J Immunol. 1970 Nov;105(5):1253–1263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill W. C., Cebra J. J. Horse anti-SI immunoglobulins. I. Properties of gamma-M-antibody. Biochemistry. 1965 Dec;4(12):2575–2584. doi: 10.1021/bi00888a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurlimann J., Darling H. In vitro synthesis of immunoglobulin-A by salivary glands from animals of different species. Immunology. 1971 Jul;21(1):101–111. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLINMAN N. R., ROCKEY J. H., KARUSH F. EQUINE ANTIHAPTEN ANTIBODY II. THE GAMMA-G(7S-GAMMA) COMPONENTS AND THEIR SPECIFIC INTERACTION. Immunochemistry. 1965 Mar;47:51–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klinman N. R., Rockey J. H., Frauenberger G., Karush F. Equine anti-hapten antibody. 3. The comparative properties of gamma G- and gammaA-antibodies. J Immunol. 1966 Apr;96(4):587–595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mach J. P., Pahud J. J. Secretory IgA, a major immunoglobulin in most bovine external secretions. J Immunol. 1971 Feb;106(2):552–563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConahey P. J., Dixon F. J. A method of trace iodination of proteins for immunologic studies. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1966;29(2):185–189. doi: 10.1159/000229699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuire T. C., Van Hoosier G. L., Jr, Henson J. B. The complement-fixation reaction in eguine infectious anemia: demonstration of inhibition by IgG (T). J Immunol. 1971 Dec;107(6):1738–1744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pahud J. J., Mach J. P. Equine secretory IgA and secretory component. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1972;42(2):175–186. doi: 10.1159/000230604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pahud J. J., Mach J. P. Identification of secretory IgA, free secretory piece and serum IgA in the ovine and caprine species. Immunochemistry. 1970 Aug;7(8):679–686. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(70)90174-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perryman L. E., McGuire T. C., Banks K. L., Henson J. B. Decreased C3 levels in a chronic virus infection: equine infectious anemia. J Immunol. 1971 Apr;106(4):1074–1078. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter P., Noakes D. E. Immunoglobulin IgA in bovine serum and external secretions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Jul 27;214(1):107–116. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(70)90074-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROCKEY J. H., KLINMAN N. R., KARUSH F. EQUINE ANTIHAPTEN ANTIBODY. I. 7S BETA-2A- AND 1OS GAMMA-1- GLOBULIN COMPONENTS OF PURIFIED ANTI-BETA-LACTOSIDE ANTIBODY. J Exp Med. 1964 Oct 1;120:589–609. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.4.589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raynaud M., Iscaki S., Mangalo R. Séparation chromatographique des gamma G et gamma A antitoxines antidiphtériques de cheval. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1965 Oct;109(4):525–551. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rockey J. H. Equine antihapten antibody. The subunits and fragments of anti-beta-lactoside antibody. J Exp Med. 1967 Feb 1;125(2):249–275. doi: 10.1084/jem.125.2.249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouse B. T., Ingram D. G. The total protein and immunoglobulin profile of equine colostrum and milk. Immunology. 1970 Dec;19(6):901–907. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANDOR G., KORACH S., MATTERN P. 7S GLOBULIN, IMMUNOLOGICALLY IDENTICAL TO 19S GAMMA-1 (BETA-2)-M-GLOBULIN, A NEW PROTEIN OR HORSE SERUM. Nature. 1964 Nov 21;204:795–796. doi: 10.1038/204795a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandor G., Audibert F. Deux fonctions physiologiques de l'immunité humorale et les deux protéines qui l'assument dans le sérum de cheval. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1970 Mar 16;270(11):1538–1540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultze H. E., Haupt H., Heide K., Heimburger N., Schwick H. G. Comparative investigations of purified diphtheria and tetanus T-components and their fragments. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):273–284. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90007-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasi T. B., Jr Structure and function of mucosal antibodies. Annu Rev Med. 1970;21:281–298. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.21.020170.001433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaerman J. P., Heremans J. F. Immunoglobulin A in the pig. I. Preliminary characterization of normal pig serum IgA. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1970;38(6):561–572. doi: 10.1159/000230312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaerman J. P., Heremans J. F., Van Kerckhoven G. Communications. Identification of IgA in several mammalian species. J Immunol. 1969 Dec;103(6):1421–1423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaerman J. P., Querinjean P., Heremans J. F. Studies on the IgA system of the horse. Immunology. 1971 Sep;21(3):443–454. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir R. C., Porter R. R. Comparison of the structure of the immunoglobulins from horse serum. Biochem J. 1966 Jul;100(1):63–68. doi: 10.1042/bj1000063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir R. C., Porter R. R., Givol D. Comparison of the C-terminal amino-acid sequence of two horse immunoglobulins IgG and IgG(T). Nature. 1966 Oct 8;212(5058):205–206. doi: 10.1038/212205a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YAGI Y., MAIER P., PRESSMAN D., ARBESMAN C. E., REISMAN R. E. THE PRESENCE OF THE RAGWEED-BINDING ANTIBODIES IN THE BETA-2A, BETA-2M, AND GAMMA GLOBULINS OF THE SENSITIVE INDIVIDUALS. J Immunol. 1963 Jul;91:83–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zolla S., Goodman J. W. An aggregating immunoglobulin in hyperimmune equine anti-pneumococcal sera. J Immunol. 1968 Apr;100(4):880–897. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]