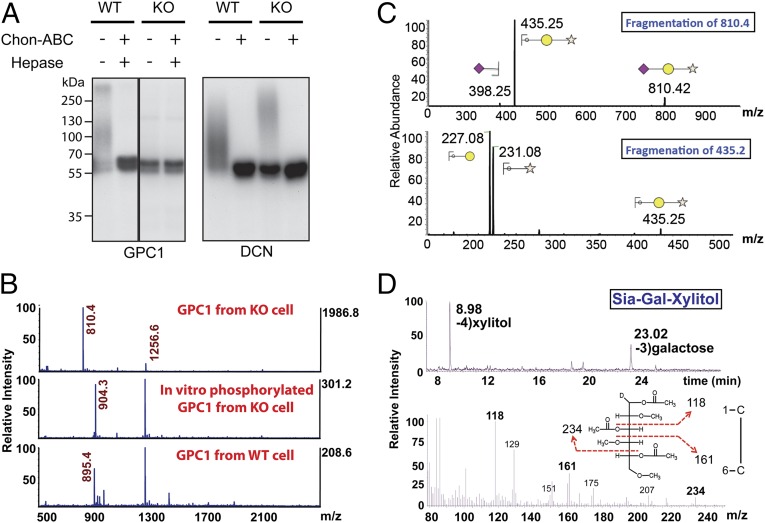
Fig. 3.
Identification of Siaα2–3Galβ1–4Xylβ1 on GAG attachment sites on proteoglycans from FAM20B deletion cells. (A) GPC1 and DCN were purified from FAM20B WT and KO cells. An aliquot of purified GPC1 and DCN was phosphorylated using recombinant Fam20B in the presence of [γ-32P]ATP, and each of the samples was then treated with or without Chon-ABC and hepase. The products were separated by gel electrophoresis and incorporated radioactivity was detected by autoradiograph. (B, Top) The MS analysis of permethylated O-linked glycans released from GPC1 purified from FAM20B KO cells (unphosphorylated). (Middle) The MS analysis of FAM20B KO GPC1 glycans that were phosphorylated by Fam20B in vitro. (Bottom) MS analysis for that derived from FAM20B WT cells. Note: m/z = 1256.6 was identified as a branched O-glycan (Fig. S8 A and B). (C) Sequential fragmentation of m/z = 810.4 and m/z = 435.2 ion species and the assignment of the fragments. (D, Top) Gas chromatography profile of alditol acetates derived from hydrolyzed Sia-Gal-Xylitol and the identification of xylitol and galactose retention peaks. (Bottom) Fragmentation of galactose (retention time: 23.02 min) and the identification of signature fragment ions of C3 linked Gal (m/z = 118, 161, and 234).