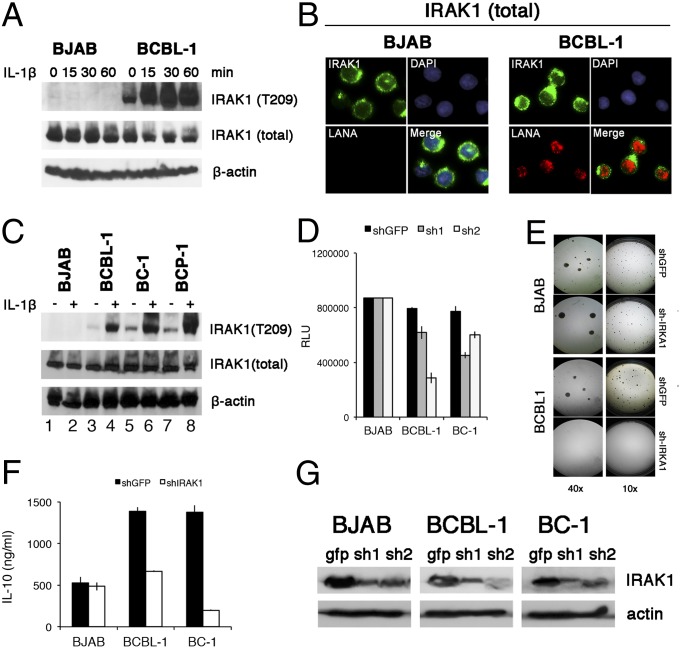
Fig. 5.
Function of mutant IRAK1 in PEL. (A) BJAB and PEL cells were stimulated with 10 ng/mL IL-1β for indicated amounts of time and protein extracts were analyzed by Western blotting, using rabbit anti-IRAK1, anti-phospho IRAK1 T209, and mouse anti-β-actin, followed by secondary HRP-conjugated antibodies. (B) BJAB and PEL cells were fixed, permeabilized, and stained with rabbit anti-IRAK1 and mouse anti-LANA monoclonal antibodies, followed by fluorescence-conjugated secondary antibody. Nucleus was stained blue with DAPI. (Magnification: 600×.). (C) A panel of PEL cell lines and the BJAB Burkitt lymphoma cell line were stimulated with 10 ng/mL IL-1β for 30 min and analyzed as in A. (D) Cells viability was analyzed with a CellTiter-Glo kit. BJAB and PEL cells were infected with two independent shRNA-lentiviruses against IRAK1 for 4 d, and luminescence was measured. GFP shRNA lentiviruses were used as negative controls. (E) Result of colony formation assay at 10× and 40× magnification of BJAB and BCBL-1 cells infected with IRAK1 shRNA lentivirus vector and cultured under 5 µg/mL puromycin selection for 3 weeks. (F) Reduction in secreted IL-10 accumulated for 4 d after infection with anti-IRAK1 or anti-GFP shRNA for indicated cell lines. (G) Western blot of IRAK1 levels at 4 d after infection with anti-IRAK1 or anti-GFP shRNA for indicated cell lines.