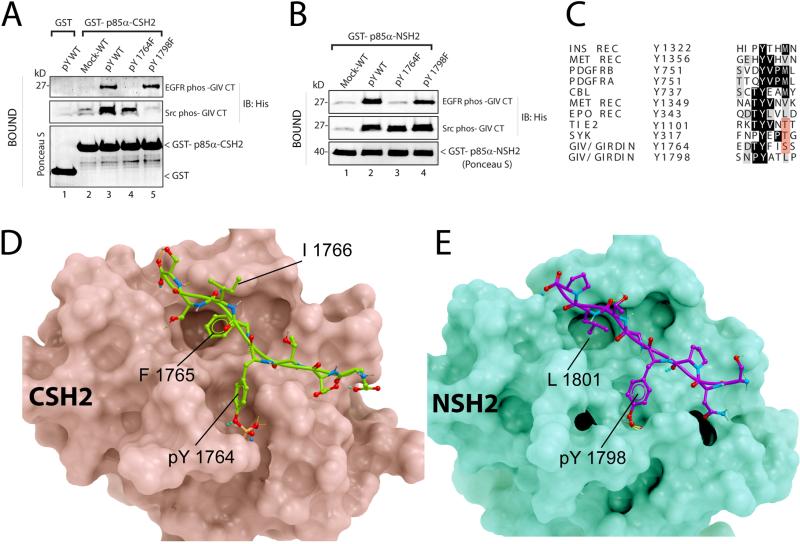
Figure 4. Structural basis for the GIV-p85α interaction.
A. His-GIV CT wild-type (pY-WT) and single tyrosine mutants (pY1764F and pY1798F) were phosphorylated in vitro with recombinant EGFR or Src and used in pulldown assays with GST-p85α-CSH2 or GST immobilized on glutathione beads. Bound proteins were immunoblotted for His-GIV CT. B. In vitro phosphorylated His-GIV CT wild-type (pY-WT) and single tyrosine mutants (pY1764F and pY1798F) were used in pulldown assays with GST-tagged N-terminal SH2 domain of p85α (GST-p85α-NSH2). C. The sequence flanking Tyr1764 in GIV was aligned with phosphopeptide-binding sites on other p85α-interacting proteins. D, E. Proposed structures of complexes between the C-terminal SH2 domain of p85α (D, pink) and GIV-derived phosphopeptide EDTpY1764FISS (D, green), and between the N-terminal SH2 domain of p85α (E, green) and GIV-derived phosphopeptide SNPpY1798ATLP (E, magenta) are shown. No steric clashes were observed in either model. Detailed views and descriptions of the predicted contacts, Fig S6.