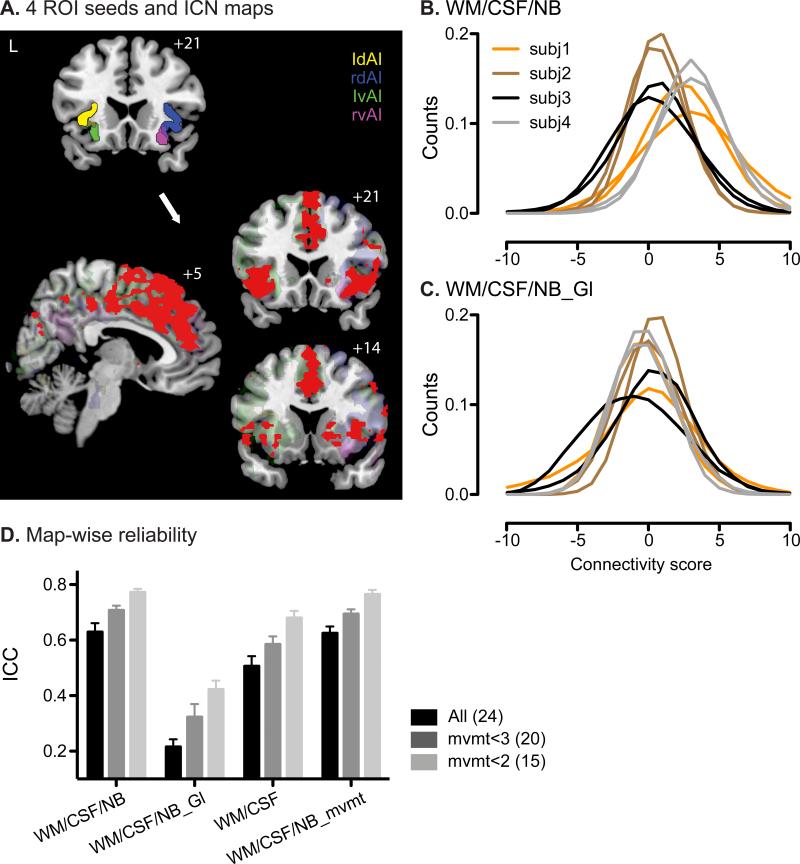
Figure 1. ICNs generated by seed-based ROI analysis and their map-wise reliability.
A. The four anterior insular (AI) clusters used as ROI seeds (upper left image; left dorsal AI, ldAI – yellow; right dorsal AI, rdAI – blue; left ventral AI, lvAI– green; right ventral AI, rvAI – magenta) and their corresponding group-level functional connectivity maps, threshold at t > 7, cluster size > 300 voxels (lower images; individual maps are in transparent colors corresponding to their ROI seeds; overlap of all four maps is in red). B. Distributions of gray matter voxels’ connectivity scores from the ROI analysis using right ventral AI as the seed. White matter, CSF and non-brain signals were included as nuisance regressors. For visual clarity, data from four representative subjects are shown. Lines of the same color represent data from the two scans of the same subjects. C. Same as B, except the global signal was included as a nuisance regressor, in addition to white matter, CSF and non-brain. Data are from the same four subjects as in B. D. Average map-wise ICC across the four ROI analyses for all subjects (black), mvmt<3 (gray) and mvmt<2 (light gray) groups. Number of subjects in each group is indicated in parentheses. Error bars signify s.e.m across the four ROI analyses. Nuisance regressors included in the analyses are indicated along the x-axis. WM, white matter; NB, non-brain; Gl, Global signal; mvmt, movement parameters.