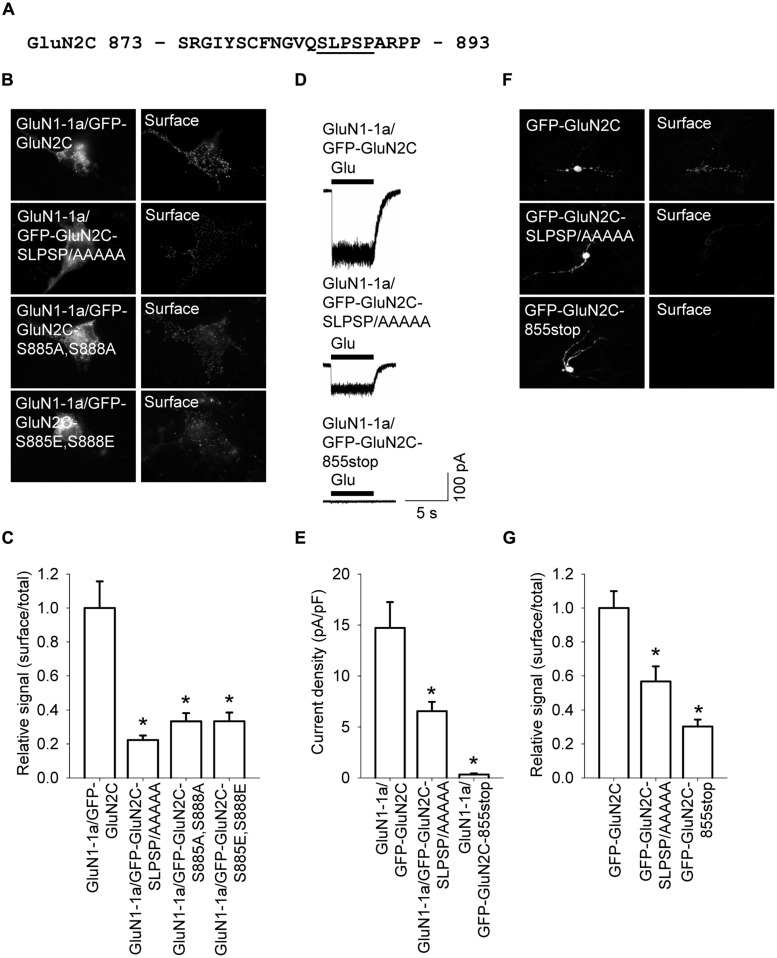
FIGURE 6.
A short amino acid sequence in the proximal C-terminus of GluN2C is essential for surface delivery of NMDA receptors. (A) The amino acid sequence of the proximal part of the C-terminus of GluN2C; the residues that were replaced with alanines are underlined. (B) Representative images of total (left panel) and surface (right panel) pools of NMDA receptors expressed in COS-7 cells. (C) Summary of the normalized ratios of surface and total expression of the indicated NMDA receptor subunits measured using fluorescence microscopy. *p < 0.05 (relative to GluN1-1a/GFP-GluN2C); ANOVA. (D) Whole-cell voltage-clamp recordings were performed in HEK293 cells expressing the indicated NMDA receptor subunits. Currents were elicited by applying a 5-sec pulse of 1 mM glutamate (indicated by the filled bar); representative traces are shown. (E) Quantitative analysis of the peak current density (pA/pF) mediated by the indicated NMDA receptors; n ≥ 19. *p < 0.05 (relative to GluN1-1a/GFP-GluN2C); ANOVA. (F) Representative images of total (left panel) and surface (right panel) GluN2 pools in CGCs. (G) Summary of the normalized ratios of surface and total expression of NMDA receptor subunits measured using confocal microscopy. *p < 0.05 (relative to GFP-GluN2C); ANOVA.