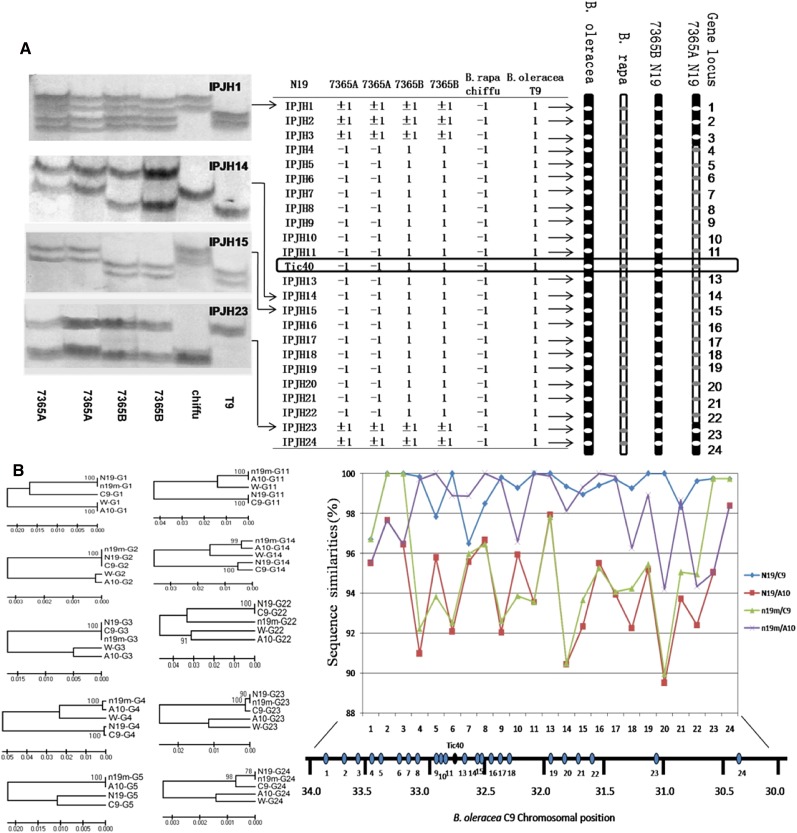
Figure 4.
Analysis of the subgenome origin of genomic regions around BnaC9.Tic40 and bnac9.tic40 in B. napus. A, Segregation of IP molecular markers on linkage group N19 of B. napus 7365A and 7365B. Twenty-three IP molecular markers (IPJH1–IPJH24) corresponded to 23 loci flanking Tic40 in B. rapa A10 and B. oleracea C9 (Supplemental Table S3). For IPJH1, IPJH14, IPJH15, and IPJH23, amplification patterns are shown on the left. For each molecular marker, numbers were assigned to polymorphic fragments: −1 if they were identical to those from B. rapa Chiffu and +1 if they were identical to those from B. oleracea T9. The presence of these fragments in B. napus 7365A and 7365B is shown in the center table, and the result is visualized on the right, with white ovals representing C genome alleles and gray ovals representing A genome alleles. For gene loci IPJH1, IPJH2, IPJH3, IPJH23, and IPJH24, 7365A and 7365B displayed the expected pattern with fragments from both Chiffu and T9 (e.g. IPJH1 and IPJH23). However, for loci IPJH4 to IPJH22, B. rapa-specific fragments were present in 7365A; conversely, for IPJH13 and IPJH14, B. oleracea-specific fragments were present in 7365B. B, Sequence divergence of homologs of 23 flanking genes. The approximate genomic locations of the flanking genes at B. oleracea C9 are indicated by ovals (bottom right). In both 7365A and 7365B, partial sequences (300–800 bp) of 23 flanking genes were aligned with their orthologs in B. rapa A10 and B. oleracea C09. Phylogenetic trees of homologs of several flanking genes constructed by MEGA4.0 are shown on the left. Sequence divergences between these homologs are shown on the right. A10, Homologs from B. rapa; C9, homologs from B. oleracea; G1 to G24, gene loci 1 to 24 flanking Tic40; N19, homologs from 7365B; n19m, homologs from 7365A; W, homologs existing in both 7365B and 7365A, representing homologs from other syntenic regions. For genes G1, G2, G3, G23, and G24, sequences from N19 and n19m cluster together with the sequence from C9. For the other genes, only N19 sequences cluster with C9 sequences, while n19m sequences cluster with those from A10, supporting the conclusion that the region around Tic40 on N19 in 7365A is derived from N10 (corresponding to A10).