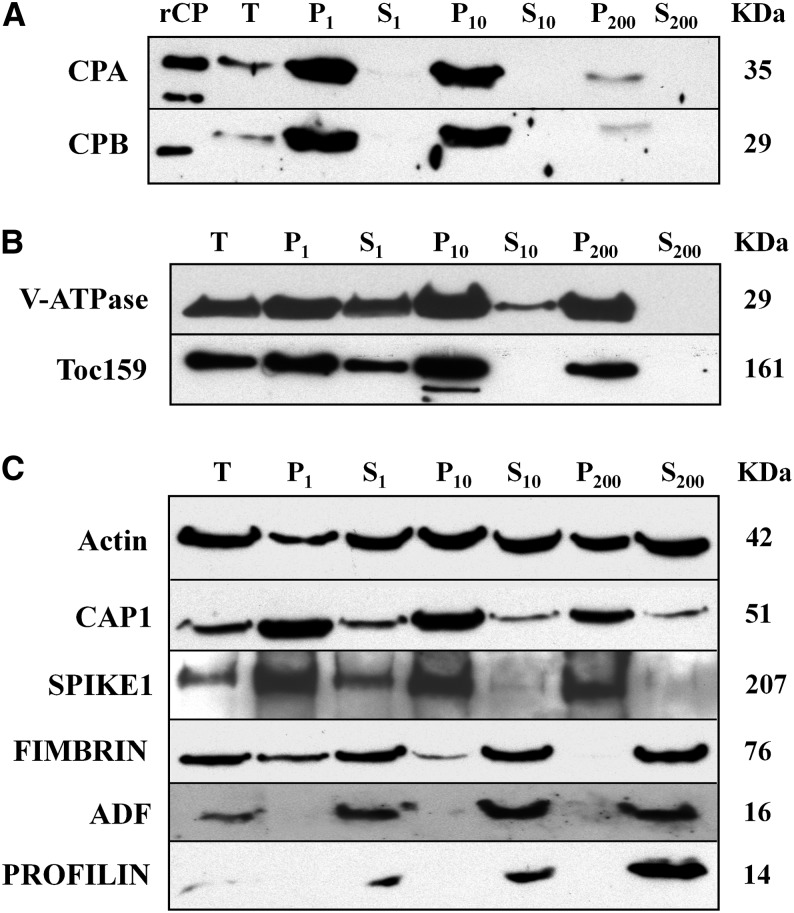
Figure 3.
CP is present in membrane fractions after differential centrifugation of cellular extracts. Analysis of CP and several other ABPs during differential centrifugation of extracts prepared from 20 DAG Arabidopsis Col-0 seedlings. The individual lanes represent the pellet (P) and supernatant (S) fractions obtained after total cellular extracts (T) were subjected to differential centrifugation at 1,000g, 10,000g, and 200,000g, respectively. Lanes were loaded with equal amounts of protein (75 µg), separated by SDS-PAGE, and immunoblotted with antibodies against CP, V-ATPase, AtToc159, and various ABPs. The molecular weight in kilodaltons for each polypeptide is given at right. A, CPA and CPB were most abundant in the pellet fractions and were virtually undetectable in the soluble fractions. rCP loaded in the first lane verifies the size of the native protein in extracts. B, Antibodies against the tonoplast marker V-ATPase and the chloroplast outer envelope protein Toc159, were used as positive controls for differential centrifugation of membrane-associated proteins. C, Actin and several cytoskeletal-associated proteins also partitioned with membranes or organellar fractions. Antibodies were used to detect the following: actin; CAP1; the ROP-GEF, SPK1; an actin filament cross linking protein, FIMBRIN; and, two actin monomer-binding proteins, ADF and PROFILIN. Actin partitioned almost equally between soluble and pellet fractions, whereas CAP1 and SPK1 were mainly in pellet fractions. By contrast, FIMBRIN, ADF, and PROFILIN were predominantly soluble proteins.